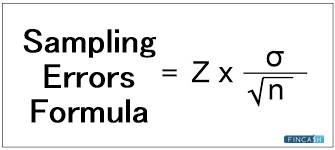Table of Contents
Sampling
Sampling definition is referred to as the process that is utilized in the field of statistical analysis. In the given process, a predefined number of observations are obtained from some larger population. The methodology is utilized for sampling from some larger population is known to depend on the specific type of analysis that is being carried out. At the same time, it might also include systematic sampling or random sampling.
How is Sampling Used?
A CPA or Certified Public Accountant known for performing the financial audit tends to make use of sampling for determining the overall completeness and accuracy of the respective account balances in the financial statements. The process of sampling that is performed by some auditor is known as audit sampling.
It is important to perform audit sampling when the given population, in the given case information related to the Accounting transaction, tends to be large. Moreover, managers within the organization might use customer sampling for assessing the demand for all-new products or the overall success of the respective marketing efforts.
Sample Size Formula
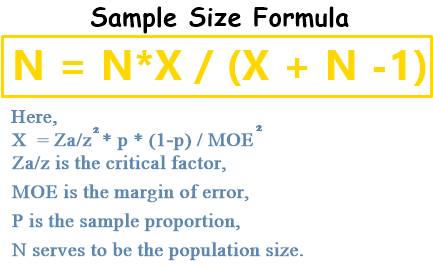
The selected sample should be the fair representation of the whole population. When a sample is being taken from some large population, it is vital to consider the manner in which the sample is selected. For getting access to the representative sample, it is expected to be drawn in a random fashion while encompassing the entire population. For instance, a lottery system can be utilized for determining the students’ average age in a university by performing sampling 10 percent of the body of the student.
Talk to our investment specialist
Sampling Types
Random Sampling
With this technique of sampling, every item within the given population tends to feature an equal probability of getting selected. It is removed the furthest from any prospective bias as there is no involvement of any human judgment in the selection of the sample.
For instance, a random sample could include selecting the names of around 25 employees out of the organization having 250 employees. The entire population is 250 employees, and the sample tends to be random as every employee out there tends to possess an equal opportunity of being selected.
Judgment Sampling
Auditor judgment can be utilized for selecting the sample from the greater population. An auditor can only be regarded about transactions that might be of the material nature. For instance, let us imagine that the auditor would be setting the materiality threshold for transactions related to accounts payable at INR 10,000. If the client is providing a complete list of around 15 transactions over INR 10,000, then the auditor might consider reviewing all transactions because of the smaller size of the population.
Some of the other types of sampling out there are simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, clustered sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and so more.
However, human judgment used in case of sampling is always known to come with a prospective for bias –whether implicit or explicit.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.