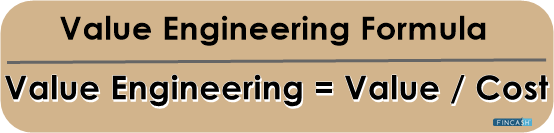
Genetic Engineering
What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is artificial manipulation and recombination of DNA to alter the genetic makeup of an organism. Typically, humans have manipulated genomes indirectly by controlling breeding and choosing offspring with desired traits.
Genetic engineering involves the direct controlling of one or more genes. Usually, a gene from another species is added to an organism to give it the desired phenotype. The techniques of genetic engineering are used for the following purposes:
- Prevention of genetic abnormalities
- Construction of genetically modified plant species
- It is used to produce therapeutic drugs
- Used for economically important plant species
- Abiotic and biotic stress-resistant plant species
Types of Genetic Engineering
1. Recombinant DNA
Under recombinant DNA technology, an artificial DNA molecule is constructed by ligating two different DNAs by using physical methods. The genes of interest are inserted into the plasmid vector and used for gene transfer experiments
Talk to our investment specialist
2 .Gene Delivering
The Gene delivering technique is used for the insertion of a gene of interest in the host genome. Under gene delivering, some methods are used for electroporation, solicitation and viral vector-mediated gene transfer, liposome-mediated gene transfer and transposon-mediated gene transfer.
3. Gene Editing
A gene-editing technique is used for the genome in which an undesired DNA sequence is removed and a new gene can be inserted into the host genome. For gene editing, some of the best tools used in gene therapy experiments are CRISPR-CAS9, TALEN and ZFN.
Process of Genetic Engineering
The process of genetic engineering is divided into five broader steps:
- Selecting and isolating the candidate gene
- Choosing and constructing the plasmid
- Transformation of gene
- Insertion of DNA into the host genome
- Confirmation of insert
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.