High-Low Method: Meaning
There are three categories of costs in every business: Fixed Cost, variable cost, and mixed cost. The high-low method is a way of separating fixed and variable costs from overall costs. The basic idea is to gather costs at a high and low activity level and then divide the fixed and variable cost components from this data.
The notion is essential in pricing research and budgeting. It can be used to figure out the following:
- Fixed and variable costs of a product
- Product line
- Machine
- Store
- Geographic sales region
- Subsidiary
- Client
High-Low Method Formula
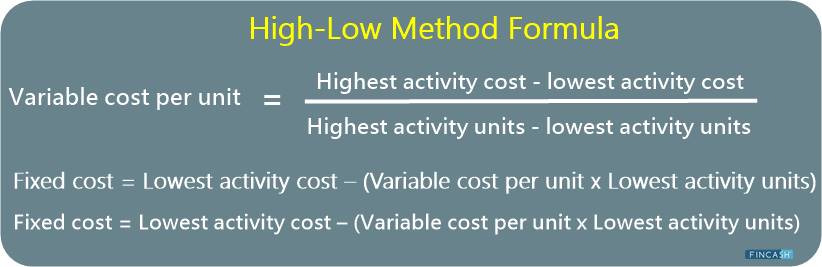
The following is the formula for creating a cost model using the high-low method:
Variable cost per unit = Highest activity cost - lowest activity cost/ Highest activity units - lowest activity units
Once you've calculated the variable cost per unit, then the fixed cost is calculated
Fixed cost = Highest activity cost – (Variable cost per unit x Highest activity units)
Fixed cost = Lowest activity cost – (Variable cost per unit x Lowest activity units)
The following is the cost model that would emerge from utilising the high-low method:
Fixed cost + variable cost x Unit activity = Cost model
High-Low Method Example
Let's understand this concept with an example. Suppose ABC International costs INR 50,000 to make 10,000 green widgets in June and INR 35,000 to generate 5,000 green widgets in July.
As there was an incremental change of INR 15,000 and 5,000 units between the two periods, the variable cost per unit in July must be INR 15,000 divided by 5,000 units, or INR 3 per unit. It can be determined that INR 15,000 of the expenditures incurred in July were variable, and the remaining INR 20,000 in costs were fixed.
Benefits of High-Low Method
Listed below are the benefits of the high-low method:
- This method is simple to implement and comprehend
- This approach just requires two data values to generate the cost behaviour
- The computation does not need the use of complicated tools or programmes
- This method also makes it simple for analysts and accountants to determine future unit costs
Limitations of High-Low Method
The high-low method is a widely used method for determining how much of a cost is constant and how much is fluctuating. However, this method comes with the following set of limitations:
- Small factors, like cost fluctuation, are ignored by the high-low technique
- It assumes constant fixed and unit variable costs, which isn't usually the case in real life
- Other costs estimating tools are also available that can offer more precise answers
- The least-squares regression approach optimises a cost estimate by taking into account all data points
- It can be used to get considerably better estimates than the high-low approach in a concise amount of time
The Bottom Line
The high-low technique is straightforward, simple to comprehend, and quick to implement. This method does not necessitate the use of complicated tools or programming. However, there are a number of drawbacks that restrict how useful this tool could be. It is imperative to be cautious while utilising this tool since it is more likely to produce erroneous findings as the cost is influenced by a number of factors and can't be accurately predicted with simply two variables.
Furthermore, at a given level of output, more fixed investment is required, which is not accounted for in this model. As a result, adopting this procedure should be done with the utmost consideration.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.