What is the Law of Supply and Demand?
The Law of Supply and demand definition is one of the fundamental concepts of microeconomics. Basically, it is a theory that states the contact between the buyer of the commodity and the seller. The theory is mainly used to explain the relationship between the demand, supply, and prices of the commodity.
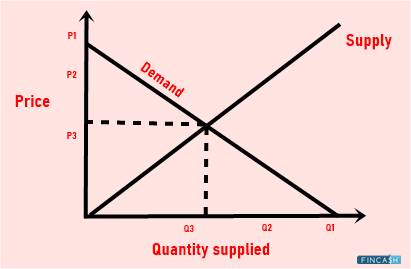
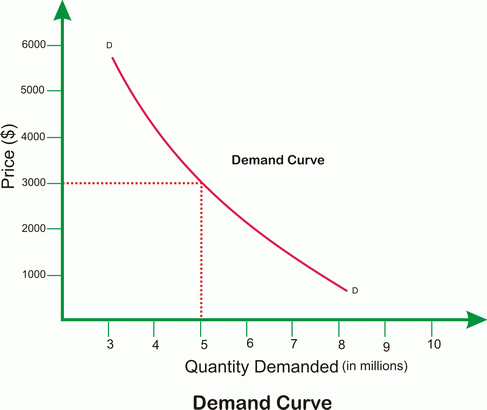
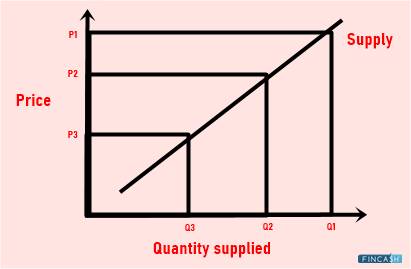
It suggests the movement of the supply and Demand Curve based on the prices.
The law of Demand Vs Law of Supply
Basically, Economics focuses on the two major laws that help people analyze the price of the product. They are:
The Law of Demand suggests that the demand for the commodity increases when its price goes down. Similarly, the higher price of the product can have a negative impact on demand. In other words, the demand and price of the commodity and inversely related to each other.
It states that there is a direct relationship between the price of the commodities and its supply. The seller is highly likely to bring more products into the Market when the price of the same increases. Similarly, they can withhold these products if the prices of the same are low. The supply of the product is always fixed. However, the supplier could change the decision concerning the quantity of product they must bring to the market. That’s done to achieve the price level the supplier wants. The higher the price of the product, the more products the supplier brings to the market for higher profits.
Talk to our investment specialist
The law of supply and demand is applicable to all types of commodities in the market. These laws act as the foundation of other economic principles. The supply and demand graph reaches the equilibrium state when the demand for the product equals the supply of the same. Simply put, when the sellers offer exactly the same quantity of the product that the customer demands, then the law of supply and demand reaches the equilibrium state. In the real-world, the equilibrium state is not achieved. That’s because there are multiple factors that play an integral part in affecting the supply and demand.
Factors Affecting Supply and Demand
As mentioned above, many factors can affect the supply and demand curves. When it comes to demand, customer preferences and the latest trends are the most common reasons for the shifts in the demand curve. The demand is also affected by the availability of substitute goods. If the substitute is available at a lower price, then it will attract high demand and vice versa. Other factors include seasonal changes, Inflation, change in the customers’ Income, and advertising.
The main Factor that affects the supply curve is the production cost. The technology could also lead to a shift in the supply curve. If the material and labor cost increases, then the supplier might not be able to produce large quantities of the product. Other factors affecting the supply of the commodity are Taxes, institution cost, and political changes.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.