Everything About e-Way Bill
The Electronic-Way Bill, shortly known as e-Way Bill, is referred to a Receipt or report that a carrier issues, stating the specifications and instructions for the transportation of a consignment of goods. In this receipt, the person moving goods worth more than Rs. 50,000, whether interstate or intrastate, uploads the appropriate information and data before shipping goods.

An e-Way bill is generated using a digital interface or software on the GST portal. In this post, you get to find out more about what is an e-Way bill and how you can generate e-way bill.
Latest News and Updates on e-Way Bill
According to the latest news and updates on e-Way bill, here are some key points that must be considered:
According to the e-Way bill portal's release notes, a suspended GSTIN cannot create an e-Way bill. On the contrary, the arrested person can receive a generated e-Way bill as a receiver or as a transporter.
The method of transport 'Ship' has now been modified to 'Ship/Road cum Ship,' allowing the user to input a vehicle number for goods first carried by road and a bill of lading number and date for goods initially moved by ship. This will aid in obtaining ODC incentives for ship-based mobility and make updating vehicle information easier as vehicles are transferred by road.
The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) said that the banning of GSTINs for e-Way Bill generation is now only considered for the defaulting supplier's GSTIN and not for the defaulting recipient's or transporter's GSTIN.
What is an e-Way Bill in GST?
The e-Way bill ensures that products being carried conform with the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law. Moreover, it is an excellent instrument for tracking the flow of goods and detecting Tax Fraud. The distance determines the validity of an e-Way bill that the goods travel.
For the transportation of goods, the e-Way bill required under the GST system has replaced the way bill was required under the VAT regime - a tangible document that had to be created to move the goods. The physical document used in the VAT regime has now been superseded with an electronically produced document under the GST regime.
Talk to our investment specialist
What does an e-Way Bill contain?
An e-Way bill highlights the following information:
- The consignor’s and the consignee’s names
- The site of origin and destination
- The purpose and the direction of the consignment
- The person in charge of the transporter of the carriage of goods must have a hard copy of the e-Way invoice
What is the Effective Date of GST e-Way Bill?
The e-Way bill under the GST regime got active for transit goods from one state to another as of April 1, 2018. For the transfer of goods within the state, an e-Way bill was introduced in phases beginning on April 15, 2018, and ending on June 16, 2018. The e-Way bill is now applicable in all states in the current year.
How to Generate e-Way Bill?
You have a variety of modes that can help you in a successful e-Way bill generated process, such as:
- By visiting the official website portal
- By using an Android app where you will have to give your registered mobile number and the IMEI of the phone
- By an SMS-based Facility with the help of the registered mobile number
- In the case of a bulk generation, a different excel based upload option is given
- The e-Way bill generates a unique e-Way Bill Number (EBN) that is made accessible on the GST website to the supplier, receiver, and transporter, who can use it to fill out Form GSTR 1
- Within 72 hours of receiving the e-Way bill, being a recipient, you must declare your acceptance or rejection of the consignment
If you don't confirm or reject the consignment within the given period, you will be believed that you have accepted the information.
When is the e-Way Bill Required?
The e-Way bill is required under the GST regime by the following people:
Registered Person
When there is a movement of items worth more than Rs 50,000 to or from a registered individual, an e-Way bill generation is mandatory. However, if the products are worth less than Rs 50,000, a registered individual or transporter could choose to create and carry an e-Way bill as per the preference, but it is not mandatory.
Unregistered Person
Unregistered Individuals must also generate an e-Way bill. When an unregistered person makes a supply to a registered person, the receiver is responsible for ensuring all compliances are met.
Transporters
The person who transports goods by road, air, rail, or other means of transport must create an e-Way bill as well if the supplier has not done so.
When is the e-Way Bill Not Required?
There are a few instances when the e-Way bill is not required, as follows:
- In case the goods are carried from the Land customs station, air cargo complex, airport, and port to an inland container depot or a container freight station for custom's clearance
- If the cargo containers being carried are empty
- If the consignor of the commodities is the State Government, the Central Government, or a local body, and the items are carried by rail
- When the goods are conveyed via a non-motorized vehicle
- If the Union Territory or GST laws state that the items being carried don't require an e-Way bill
- When the goods are carried within the same state over a distance of fewer than 10 kilometres from the transporter's place of business to the consignee's place of business
- If the consignor transfers products from a business location to where the goods must be weighed and vice versa. The maximum distance, however, must be 20 kilometres, and the delivery challan must be carried
How to Register on the E-Way Bill Portal?
As mentioned above, three sorts of taxpayers can sign up for the e-Way bill, such as:
- Registered suppliers
- Registered or unregistered carriers
- Unregistered suppliers
The following is a step-by-step registration process for taxpayers and registered transporters:
- Go to the official e-Way bill portal
- At the top of the page, click 'Registration.’ A drop-down menu will appear; from there, select 'e-Way Bill Registration'
- Enter your GST Identification Number and captcha code and click 'Go'
- Create a One-Time Password after verifying the GST details displayed on the screen
- Select 'Send OTP'
- Enter OTP received and validate it by clicking on 'Verify OTP'
- You will be taken to a new page where you can create a new user ID and password
Once the e-Way bill login credentials are generated, you can create invoices for the goods movement.
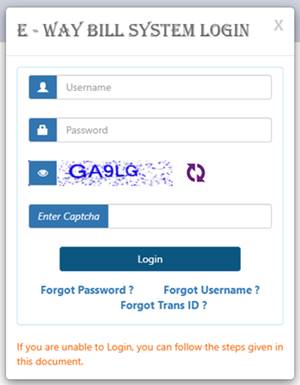
Steps to e-Way Bill Login
Once you have registered on the e-Way portal, you can login with the help of your user ID and password:
- Visit the official e-Way bill portal
- Click Login option available on the right side of the homepage
- A new pop-up will appear where you will have to add your Username and Password as generated before
- Enter the Captcha code
- Click Login
Case of Movement of Goods by a Registered Person
Suppose the registered person (a consignor), or the recipient of supplies (a consignee) moves products. In that case, regardless of the conveyance, both the consignor and the consignee can generate the e-Way Bill in Form GST EWB 01 electronically on the common portal after furnishing information in Part B of Form GST EWB 01.
If the registered individual causes the movement of goods and hands them over to the transporter for road transportation without an e-Way bill, the transporter must generate the same.
In this case, if the registered person already furnishes the details about the transporter in Part B of Form GST EWB 01, the transporter can create the e-Way bill based on the given information in Part A of Form GST EQB 01.
Case of Movement of Goods by an Unregistered Person
If an unregistered person transports goods in his conveyance, the e-Way bill must be created either by him or by the transporter. This has to be created in Form GST EWB-01 on the GST portal.
Validity of the e-Way Bill

The above image contains some validity information on the types of conveyance and the distance covered by them. While at it, you must keep in mind that there is an exception to it. If the items cannot be carried within the validity period of the e-way bill due to any extraordinary circumstances, the transporter can produce another e-Way bill after revising the data in Part B of Form GST EWB 01. This way, the commissioner can, by notification, prolong the validity term of an e-Way bill for a specific category of products.
The validity of an e-Way bill is premeditated from the date on which it was generated to the midnight of the next day. For instance, suppose you have created an e-Way bill at 4 PM on January 23; it will be valid until midnight on January 24.
Penalties on the e-Way Bill
If an e-Way bill is not generated, a penalty of Rs.10,000 could be charged. Aside from the fine, the vehicle transporting the items and the products being moved could be detained or confiscated.
The Bottom Line
Since the adoption of e-Way bills in India in April 2018, the volume of goods movements across states has surged dramatically. However, people have received financial benefits if the threshold limit for particular things falls below a certain level. For instance, the e-Way bill limit in Maharashtra 2021 was Rs. 1 lakh, which means Maharashtra exempted the generation of e-Way bills if the threshold amount was less than Rs.1 lakh.
Moreover, it has offered plenty of benefits to every type of person involved in transporting and shipping goods. So, if you have not been able to register on the e-Way bill portal yet, follow the steps mentioned above and complete the process today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is it mandatory to select the tax rate when entering the goods information?
A: No, choosing the tax rates while generating the e-Way bill is not required.
2. What if the e-Way bill has an error or incorrect entry?
A: After the e-Way bill has been generated, no changes can be made. If an error occurs, you must cancel the generated bill and create a new one.
3. How to Generate an e-Way Bill if there is no invoice?
A: If you have the required documents, such as the tax invoices, credit notes, delivery challans, and bills of supply or entries, you can easily create an e-Way bill.
4. Is it required to register in the e-Way portal if I have already registered in the GST Portal?
A: Yes, even if you have already registered on the GST website, you must register on the e-Way portal.
5. Is it possible to generate a large number of e-Way bills at once?
A: Yes, any taxpayer or transporter who has enabled the automatic invoice generation platform can create the e-Way bills in bulk.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.