
Table of Contents
Deferred Income Tax In India
Taxation in India involves a complicated structure comprising different tax regime micro units. Both companies and individuals have the responsibility of paying income tax. Deferred Income tax is a type of tax imposed mainly on enterprises. This tax is either paid or has been settled because of transient difference inconsistency between a company's tax statement and income statement.
Based on the Accounting standards, companies in India create two financial reports every Fiscal Year. One is the tax statement, while the other one is the income statement. The main reason behind creating different reports is variations in their guiding principles that govern the organization's income and taxation records. So, guidelines for taxation and income are different. As a result, numerical data shown on the reports also can vary slightly. Due to this disparity, many companies need to pay deferred tax. It may be deducted by the tax department in advance or carried over to the subsequent financial year.
What is a Deferred Income Tax Asset?
Whether you have paid the tax or need to carry it forward, it leads to deferred tax assets. You can calculate the deferred tax asset by calculating the difference between your Taxable Income and book income. For instance, a deferred tax case can arise when Indian tax authority expenses or revenues at different times. The deferred tax asset helps you reduce your company's tax liabilities in the future.
Talk to our investment specialist
Is Deferred Income Tax a Current Liability?
The term 'deferred Tax Liability' refers to the situation when you can find the difference between the deducted tax of the company and tax for accounting needs. So, the liability represents the fact that your organization may need to pay a higher income tax due to the present transaction.
There are some reasons why deferred income tax liability arises, such as:
- Most companies have more than one copy of financial statements. They are intended for personal use and for furnishing to the tax authorities. Moreover, it happens because of the difference between tax codes and accounting rules in revenue and asset Depreciation.
- Companies try to drive profits to gain optimal profits for shareholders.
- Some organizations push their current profit margin into the coming years to minimize the tax burden.
Deferred Income Tax Examples
Here's an example to illustrate deferred income tax -
Deferred tax asset example - Suppose a company, ABC manufactures smartphones. It assumes a 2% probability of sending its products for warranty repairs. The revenue of the company in 2022 is Rs. 1000000. However, it results in discrepancies between the tax authority and income statements.
Deferred tax liability example - A company ABC is a smartphone manufacturer, and it assumes their Manufacturing machines (worth Rs. 60000) last for three years. Its tax is 30% on the profits.
But, financial accounting has to consider a yearly depreciation of Rs. 20000 for the upcoming three years. So, every year, income is reduced by Rs. 20000, while tax Deduction amounts to Rs. 6000.
Again, assume that tax accounting causes depreciation of Rs. 30000 in the first year. Similarly, the depreciation amount is Rs. 20000 and Rs. 30000 in the second and third year, respectively. Thus, in the initial year, the company has a depreciation of Rs. 30000 and earns tax benefits worth Rs 9000. It results in a tax liability of Rs.3,000 (Rs. 9000 – Rs. 6000).
Deferred Income Tax Formula
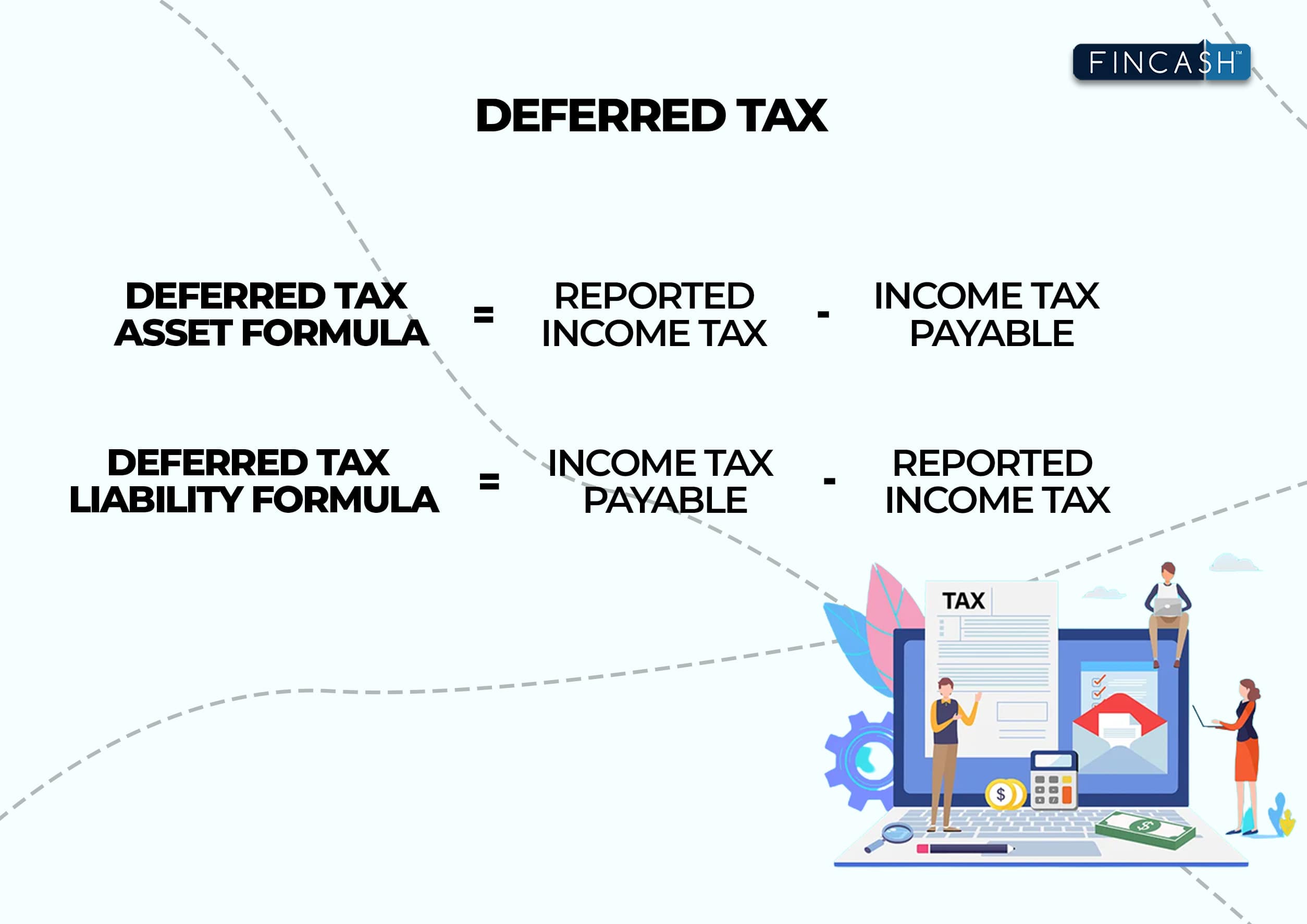
Deferred Income Tax Calculator
If you want to calculate deferred income tax, you need particulars like -
- Income
- Depreciation
- Payable Sales Tax
- Leave encashment
It helps you determine the closing balance of DTA/DTL. However, today, the calculation will become easier with the availability of calculators. Online calculators need inputs-
- Tax status
- Estimated annual taxable income
- The average yearly Tax Rate
- Assessment year
Deferred Income Tax Benefits
Tax benefits refer to how much tax benefit you can activities in the current or past periods. These benefits are because of the temporary differences between the tax and value for some items.
Conclusion
Deferred tax assets and liability items are major aspects of a company's financial statements. The term 'deferred' means postponed or delayed. The tax is due or calculated for the current period. The variance in timings leads to differences in the accounting.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.












