Table of Contents
Marginal Utility
What is Marginal Utility?
Marginal Utility is a term that refers to increased satisfaction that a consumer derives from having additional goods or services. This concept is coined by economists in order to understand how much consumers are willing to buy. In other words, economists use the concept of marginal utility is always to understand how the level of satisfaction affects the decisions of the consumer. The marginal utility curve is important to consider. The marginal utility curve is always convex to the origin.

Marginal Utility has both positive and negative utility. Positive marginal utility refers to the consumption of an extra item which increases the total utility. Whereas the negative marginal utility refers to the consumption of another unit, thereby decreasing the overall total utility.
Another concept known as the law of diminishing marginal utility has also been identified by economists. This concept deals with the understanding of how the first unit of consuming a good or service has more utility than other units to follow.
The concept of marginal utility is extremely useful when it comes to understanding and explaining how a consumer makes choices to get the largest benefits from small budgets.
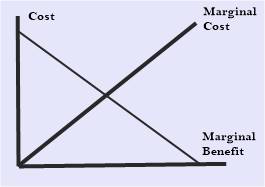
Usually, a consumer continues consuming more of a particular item as long as the marginal utility is greater than the marginal cost. In a Market that is efficient in nature, the marginal cost will be equal to the price. That is why consumers keep buying more until the marginal utility of consumption falls to the price of an item.
Types of Marginal Utility
There are three most common types of marginal utility. They are as follows:
1. Zero Marginal Utility
This refers to the situation where consuming more of a particular item does not bring any satisfaction. For eg., Laura consumes a packet of wafers. She then consumes two more packets of wafers. But the satisfaction level after having a third packet of wafers has not increased. This means the marginal utility derived from consuming wafers is zero.
2. Positive Marginal Utility
This refers to a situation where having more of a particular item brings extra happiness. For eg., Laura likes eating wafers. Having two packets of wafers might bring her additional joy. Her marginal utility of consuming wafers is positive.
3. Negative Marginal Utility
This refers to the situation where having too much of a particular item can cause harm. For eg. If Laura eats another packet of wafers after having had three of them, she can fall sick. This means the marginal utility of consuming wafers is negative.
Formula of Marginal Utility
The Formula of Marginal Utility is mentioned below:
Change in Total Utility / Change in Number of Units Consumed.
Talk to our investment specialist
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.