Table of Contents
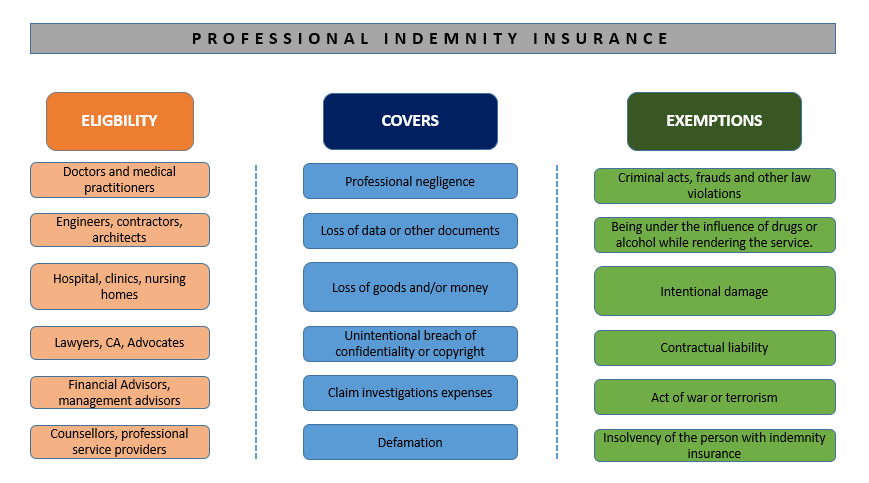
What is Inside Indemnity?
The term indemnification refers to a financial liability's security or protection. It generally takes the form of a contractual agreement between two parties in which one undertakes to compensate the other for losses or damages.

An indemnity agreement protects Board Directors and company executives from personal liability if the company is sued or suffers losses. Indemnification provisions are prevalent in business bylaws, but many Directors may want to take it a step further and have a formal agreement that cannot be modified or deleted for any reason. The contract is a direct bilateral agreement between the Director and the Corporation.
What is the Indemnity Clause?
Indemnity clauses, often known as indemnity provisions, obligate one party to pay the other for recoverable damages resulting from third-party claims. The indemnified party is obligated to make a payment demanded by the indemnifying party.
There are two types of indemnification clauses: mutual and one-sided indemnification. Mutual indemnity requires parties to compensate each other, whereas one-sided indemnification requires one side to pay. Covered events can trigger indemnity clauses.
Talk to our investment specialist
Indemnity Bond
An indemnity bond guarantees that the bond's holder will be adequately reimbursed in the event of a loss.
This bond protects the lender if the borrower fails on a legally obligated debt. If the principal fails to meet their contractual duties (as agreed between the obligee and the principal), the principal is liable for the entire bond amount (including legal costs). If a person fails to pay the agreed-upon sum, their business and personal assets will make up the difference. This is a non-negotiable relationship. The surety bond will not be approved if it is not signed.
Inside Indemnity Example
An insurance firm is a good illustration of this because the insurer or Indemnitor commits to compensate the insured or indemnitee for any damages or losses incurred over some time. The insured must pay premiums to bind the agreement so that the insurer can repay or compensate for the damages or losses.
Indemnification can be paid in cash, in the form of repairs or replacements, or any other method that the parties agree on.
Types of Indemnity
1. Express Indemnity
This is a formal agreement to indemnify, usually containing the terms and conditions that the parties must follow. Contracts such as insurance indemnity, construction, and agency contracts are examples.
2. Implied Indemnity
This is a responsibility to indemnify that emerges from circumstances or the conduct of the parties involved rather than from a written agreement. A business relationship between an agent and a principal is a good example. When the principal refuses to accept the commodities that the agent provides, the agent can sell them to others; nevertheless, if the agency incurs a loss while selling, the principal is responsible for the loss.
Importance of Indemnity
Most agreements, having an individual and a business, include indemnity; nevertheless, it also applies to corporations and governments and between governments of different countries. This provides financial protection to pay costs in the event of negligence, blunders, accidents, or other unforeseen circumstances that significantly impact the business's flow.
One approach to protecting yourself from claims or litigation is to purchase Indemnity insurance. Even if the holder is at fault, this insurance protects him from paying the total amount of a settlement. Because litigation is widespread, many corporations seek indemnity for their directors and executives. It covers legal bills, court costs, and settlements.
Conclusion
It is common to have an indemnification agreement to attract high-quality experts to serve on a Board of Directors. The indemnity agreement shields the Board Directors from any obligations, damages, or litigation that may arise due to their service on the company's board of directors. Essentially, the company undertakes to indemnify and hold the directors blameless from any liabilities that may arise due to being sued or held liable for a significant loss.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.