
Table of Contents
- What is Insurance?
- Why do you need Insurance?
- Types of Insurance
- Key Elements of Insurance
- How does Insurance Work?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- 1. What does risk pool mean?
- 2. Why should I purchase insurance?
- 3. Who stands to benefit if I purchase an insurance?
- 4. What should I look for while purchasing insurance?
- 5. What is ‘underwriting’?
- 6. Do the terms and conditions differ based on the policies I purchase?
- 7. Can I purchase more than one insurance policy?
- 8. Is there any insurance that is compulsory?
- 9. What is the importance of health insurance?
- 10. What is insurance premium?
- 11. How is the premium calculated?
- 12. Can I get back the premium if I don’t claim the insurance?
A Detailed Guide to Insurance
Everyone knows about Insurance. As a general perception, Insurance is something which keeps you or the things that you have insured sustaining a heavy financial loss. But there is a lot more to this than just a cover for something that you feel is capable of taking a damage. Let's look into this in a detailed manner.
What is Insurance?
In technical terms, it is a form of risk management in which the insured entity transfers the cost of possible loss to another entity in exchange for a small monetary compensation. This compensation is called as premium. In simple terms, it is like paying a lump-sum amount to an entity to get yourself protected from a possible future loss. Thus, when there is a case of some misfortune, the insurer aids you to get through the situation.
Why do you need Insurance?
Everyone has this question in their mind. Do I really need protection? Life is full of surprises; some good ones, some bad ones. You need to be prepared for the worst that may come to you. It helps you to have that sense of security and calmness. There can be many reasons where you might need help, like critical illness, natural disaster, unexpected death of loved ones, etc. Being adequately insured in such situations provides a significant helping hand to your financial condition. Thus, one should opt for a correct type of protection according to their needs.
Types of Insurance
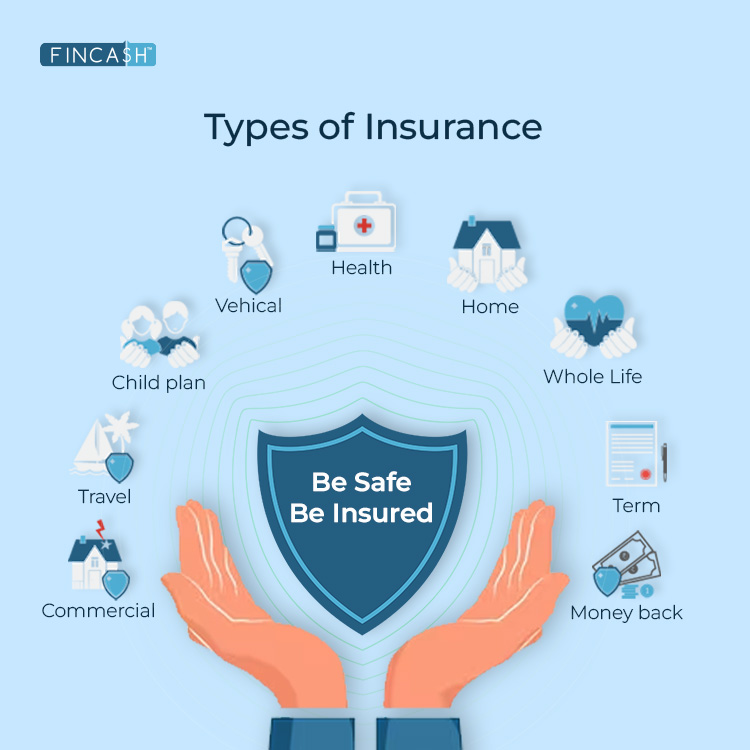
1. Life Insurance
Life protection is one of the traditional forms of insurance, designed to protect you and your loved ones from sudden calamity or disaster. It was initially designed to safeguard the Income of the families. But since then, it has evolved from being just a protection measure to an option for wealth preservation or Tax Planning. Need for a life cover is calculated on various factors like the number of dependents on a person, current savings, Financial goals etc.
2. General Insurance
Any type of coverage apart from life comes under this category. There are many different types of insurance which cover almost every aspect of your life according to your needs:
Health Insurance
It covers your medical and surgical expenses that might arise in the course of your life. Generally, health insurance provides cashless facilities in the listed hospitals.
Talk to our investment specialist
Motor Insurance
It covers the damages and liabilities associated with a vehicle (two-wheeler or four-wheeler) against various scenarios. It offers protection against damage to vehicle and covers for any third party liability stated by law against the owner of the vehicle.
Travel Insurance
It covers you from the emergencies or loss occurred during your travel. It covers you against unseen medical emergencies, theft or loss of baggage, etc.
Home Insurance
It covers the house and/or contents inside depending upon the scope of the policy. It secures the house from natural and man-made disasters.
Marine Insurance
It covers the goods, cargos, etc. from the potential loss or damage during transit.
Commercial Insurance
It offers solutions for all fields of the Industry like construction, automotive, food, power, technology, etc. The risk protection needs can differ from person to person but the basic working of an Insurance policy remains more or less the same.
Key Elements of Insurance
Here are key elements and concepts associated with insurance:
Policyholder: The person or entity that purchases an insurance policy and pays regular premiums to the insurance company is known as the policyholder or insured.
Insurance Company/Insurer: The insurance company is the entity that sells insurance policies and assumes the Financial Risk associated with covering losses or events specified in the policies.
Premium: The premium is the amount of money the policyholder pays to the insurance company at regular intervals (usually monthly, quarterly, or annually) to maintain the Insurance Coverage. Premiums can vary based on the type and amount of coverage, the policyholder's risk profile, and other factors.
Insurance Policy: An insurance policy is a legally binding contract between the policyholder and the insurance company. It outlines the terms and conditions of the coverage, including what is covered, what is excluded, the premium amount, the policy term, and other relevant details.
Life Insurance: Provides a payout to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder's death.
Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospitalization, and prescription drugs.
Property and Casualty Insurance: Protects against damage or loss of property (e.g., home, car) and liability for injuries or damage to others.
Auto Insurance: Covers damage to vehicles and liability in accidents.
business insurance: Offers protection for businesses against various risks, including property damage, liability, and business interruption.
Travel Insurance: Provides coverage for unexpected events while traveling, such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, or lost luggage.
Deductible: Some insurance policies, such as health and Property Insurance, may include a Deductible. The deductible is the amount the policyholder must pay out of pocket before the insurance company covers the remaining costs.
Claim: When a covered event or loss occurs, the policyholder can file a claim with the insurance company to request compensation or benefits as per the terms of the policy.
Underwriting: Insurance companies assess the risk associated with insuring a policyholder by evaluating factors such as age, health, driving history, and more. This process is known as underwriting, and it helps determine the premium rate.
Policyholder's Obligations: Policyholders are typically required to fulfill certain obligations, such as paying premiums on time, providing accurate information during the application process, and reporting claims promptly.
How does Insurance Work?
The most basic principle behind the concept of Insurance is 'Risk Pooling'. A large number of people are ready to get Insured against a particular loss or damage, and for that, they are ready to pay the desired premium. This group of people can be called as the Insurance-pool. Now, the company knows the number of interested people is very large and the probability of all of them needing the insurance cover at the same time is almost impossible. Thus, this allows the companies collect money at regular intervals and also settle the claim if and when such condition arrives. The most common example of this is Auto Insurance. Most car owners have a vehicle Insurance, but how many claim for it? Thus, you pay for the probability of the damage and get insured and you will be paid if the given event occurs.
So when you buy an Insurance policy, you pay a regular amount to the company as a premium for the policy. If and when you decide to make a claim, the insurer will pay out the damages that are covered by the policy. The companies use risk data to calculate the probability of the event - you are seeking insurance for - happening. Higher the probability, higher the premium of the policy. This process is called underwriting i.e. process of evaluating the risk to be insured. The company only looks for the actual value of the entity that is insured according to the Insurance contract struck between the parties. For eg., you have insured your ancestral home for 50 lakhs, the company will only consider the actual value of the house and will not entertain any emotional value the house may hold for you, as it is near impossible to put a price on emotions.
There are different terms and conditions for different policies, but the three main general principles remain the same for all types:
- Cover provided for a property or item is for its actual value and does not consider any sentiment value.
- Likelihood of a claim should spread across the policyholders so that insurers must be able to calculate the chance of risk to set the premium for the policy.
- The losses must not be deliberate.
Apart of these above pointers, below is a bit more important to understand.
An Insurance policy is a special type of contract between the insurer and the insured. It is a contract of 'utmost good faith'. This means there is an unspoken but very important understanding between the insurer and the insured person which normally do not exist in regular contracts. This understanding includes the duty of full disclosure and not to make any false or deliberate claims. This duty of 'good faith' is one of the reasons that a company might refuse to settle your claim if you have failed to notify them all the required information. And this a two-way street. The company has the 'good faith' obligations toward the client and failing to act on it can expose the insurer to a lot of trouble.
Conclusion
Every sound Financial plan is backed by risk protection. A suitable cover for you is determined by your needs and current financial situation. You should review and recheck the expenses covered in your policy and evaluate its impact on your current financial health. There are a lot of ifs and buts involved but the basic fundamentals of the working remain constant over all types of Insurance. You must be clear about what type of risk protection you are buying, why are you buying and what all is covered in the contract. It is also important for both the parties to act in 'utmost good faith' so that the whole process of insurance is crystal clear and less troublesome. And as the case with every financial product, you must be well-versed and informed about the product you are buying and get sound advice from your financial consultant.
FAQs
1. What does risk pool mean?
A: Risk pooling means small groups of individual pools with money for better insurance rates and coverage plans. The buying power improves because instead of approaching the insurance company as an individual, you are approaching it as a company. This can be made on behalf of employees by companies or by cooperative societies.
Insurance companies also carry out risk pooling. They come together to protect one another with insurance coverage that
2. Why should I purchase insurance?
A: With the help of a policy, you can effectively transfer a potential loss to the insurance company. You can do so for the exchange of a fee known as 'insurance premium.' The benefit of insurance is that it protects your savings in case of an unprecedented expense.
3. Who stands to benefit if I purchase an insurance?
A: Both the insurer and the insured stands to benefit when you purchase an insurance policy. As the insured, you are safe in the knowledge that you will be protected against a potential loss. Similarly, the insurance company uses the money you pay as a premium to create better business models and assets.
4. What should I look for while purchasing insurance?
A: When you purchase an insurance policy, you should check the premium and coverage. These should be as per your requirements.
5. What is ‘underwriting’?
A: Underwriting is a service provided by insurance companies where the firms act as guarantors to insured individuals. However, insurance companies can ask individuals seeking underwriting services to provide them with shares or prosperities as security deposits.
6. Do the terms and conditions differ based on the policies I purchase?
A: Yes, the policy's terms and conditions will differ depending on the type of insurance policy you purchase. The two main types of insurances are life insurance and Home insurance. Under general insurance comes health, travel, home, corporate, and vehicle insurance. Depending on the policy you purchase, your terms, conditions, and the premiums payable will differ.
7. Can I purchase more than one insurance policy?
A: Yes, an individual can purchase different types of policies. There are also no limitations to the number of life insurance policies that an individual can purchase. However, for a vehicle, you will need to purchase only one vehicle insurance policy.
8. Is there any insurance that is compulsory?
A: Yes, for owners of vehicles, it is compulsory to purchase a vehicle insurance policy. Otherwise, you will get into legal hassles.
9. What is the importance of health insurance?
A: A health insurance policy or medical insurance will protect you against unprecedented medical or hospitalization expenses. If you purchase medical insurance, your savings will be protected, in case you have to be hospitalized suddenly. All expenses, such as doctor's fees, hospitalization charges, ambulance fees, OT charges, and medicine, will be covered under the insurance policy. Thus, your savings will be protected.
10. What is insurance premium?
A: An insurance premium is an amount that the insured individual has to pay periodically to the insurance company to purchase the policy. When you purchase an insurance policy, the risk is transferred to the company. Hence, the company charges a fee, which is known as an insurance premium.
11. How is the premium calculated?
A: Insurance companies use mathematical calculations and statistics to evaluate the value of insurance premiums they will charge their clients. Different parameters are used for calculating premiums for different insurance policies. For example, while calculating the premium for a medical insurance policy, age, health, medical history, and other similar factors are considered. Similarly, for other insurance policies, life history and credit scores are taken into consideration.
12. Can I get back the premium if I don’t claim the insurance?
A: If you cancel your life insurance policy after having paid the premiums regularly, you can claim a refund of the premiums at least partially. However, it will depend on the terms and conditions of the insurance policy. But you cannot claim the premium on the expiration of the policy.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.
You Might Also Like













Use full and important Awareness about health insurance
Very Nice Content