Table of Contents
A Guide to CIBIL Score Range
The Credit Information Bureau India Limited (CIBIL) score is a pivotal numerical indicator that profoundly influences your financial journey. CIBIL has emerged as a prominent credit bureau, providing a comprehensive and standardised measure of an individual's creditworthiness. This three-digit numerical representation, ranging from 300 to 900, encapsulates a person's credit history and is a critical Factor lenders consider when evaluating loan applications.
The Significance of the CIBIL Score
Imagine the CIBIL Score as a financial report card, summarising your credit behaviour and payment history. It serves as a key determinant for lenders, helping them assess the risk of extending credit to you. The higher the Credit Score, the lower will be the risk, and vice versa. This crucial metric shapes financial outcomes, from securing a credit card to obtaining a mortgage.
The Components of the CIBIL Score
Understanding the components contributing to the CIBIL score is essential for individuals aiming to navigate the complex realm of credit. The primary factors include:
Payment History (35%): The most substantial component, payment history, reflects how consistently you've met your credit obligations. Timely payments positively impact, while late payments and defaults can significantly lower your score.
Credit Utilisation (30%): This factor measures the proportion of your available Credit Limit that you're currently using. Keeping credit utilisation low indicates responsible financial behaviour.
Length of Credit History (15%): The duration of your credit history influences your score. A more extended credit history provides a comprehensive overview of your financial habits.
Types of Credit (10%): A diverse mix of credit types contributes positively to your score.
Recent Inquiries (10%): Every time you apply for new credit, it triggers an inquiry. Numerous recent inquiries may be viewed as a red flag, potentially impacting your score.
Check credit score
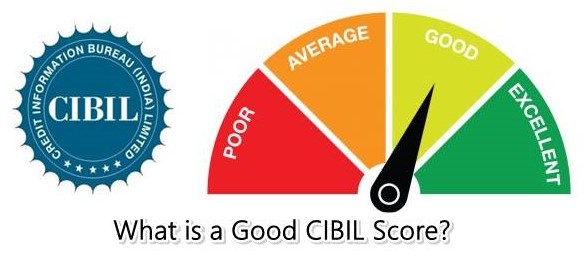
The CIBIL Score Range

The CIBIL score Range offers a spectrum that categorises individuals based on their creditworthiness:
NA/NH (No Applicable or No History)
You haven't utilised a credit card or taken out any loans, resulting in the absence of a credit history.
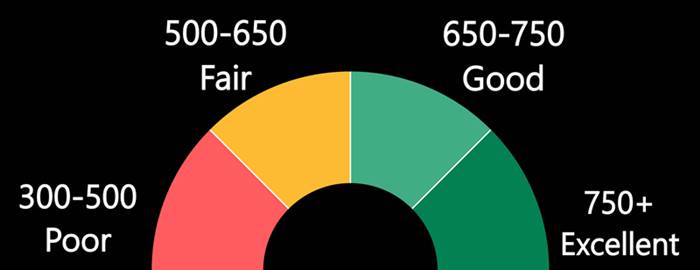
300 - 630 (Poor)
Individuals in this range may encounter difficulties securing credit. It suggests a history of missed payments, defaults on EMIs or credit card bills, poor credit utilisation, high credit inquiries, and late payments, necessitating efforts to rebuild credit. Lenders may view you as prone to loan defaults, potentially leading to your loan or credit applications not receiving approval.
631 - 705 (Average)
A fair score indicates a mixed credit history. While not as challenging, individuals in this range may face limitations in obtaining favourable credit terms. Irregular or delayed payments on credit card bills/EMIs or numerous credit inquiries could label you as a risk to lenders. Many financial institutions may decline your loan applications, and those willing to approve may impose higher interest rates and down payments.
780 - 900 (Good)
This range opens doors to attractive credit offers, signaling low risk. Consistent credit payments, a lengthy credit history, and responsible repayment behaviour designate you as a low risk for lenders. You are likely to receive credit approvals and secure favourable terms on loans. Sustaining financial prudence is essential for preserving this advantageous position.
800 - 900 (Excellent)
The pinnacle of creditworthiness, an excellent score, provides access to credit at the most favourable terms. Your outstanding financial management, consistent credit payments, minimal credit utilisation, and exemplary credit history position you as an extremely low risk for lenders. Banks and lending institutions are inclined to offer you the most favourable rates and terms on loans and credit cards. Unwavering financial discipline is vital for retaining this exceptional standing.
Influencing Factors on CIBIL Score
Numerous factors can impact credit scores, either in a positive or negative direction.
Positive Factors Affecting Credit Scores
- Timely payments on credit card dues
- On-time repayment of loan EMIs
- Settling the entire outstanding balance rather than just the minimum due
Negative Factors Affecting Credit Scores
- Non-payment or delayed payment of credit card bills and loan EMIs
- Utilising the full credit limit or consistently exceeding 75% of the credit limit on credit cards
- Holding excessive lines of credit, particularly unsecured forms
How Does Your Credit Score Influence the Borrowing Process?
Your credit score is a vital factor in determining the outcome of your loan application. Lenders scrutinise your credit score to evaluate the risk involved in extending credit to you, which can result in the approval or rejection of your application. The CIBIL Score is a tool for lenders to comprehend your credit history and assess the potential risks associated with providing you with a line of credit. Let's delve into how your credit score impacts the borrowing process.
Excellent Credit Score
An 'Excellent' credit score signifies that the borrower has consistently made timely payments on loan instalments and credit card bills, with no negative marks on the Credit Report. Lenders perceive individuals with excellent credit scores as low-risk borrowers. This credit profile opens doors to various loan benefits, including quick approval, relatively lower interest rates, and favourable terms across a spectrum of credit products.
Good Credit Score
The majority of individuals fall into the 'Good' credit score category. People in this range have favourable chances of obtaining loan approval, indicating their reliability as borrowers. However, the risk factor still exists. Depending on the lender, borrowers may or may not receive as many credit benefits as they might anticipate. To maximise credit benefits, individuals can enhance their credit score and apply for credit only when necessary.
Fair Credit Score
A fair credit score suggests borrowers have maintained a moderate track record in handling loan payments and credit card bills. They are at a higher risk of facing loan rejections, and even if approved, the terms and conditions may not be as favourable. Loans might have higher interest rates, substantial down payments, and fewer or no additional benefits. It is advisable for individuals with a fair credit score to focus on rebuilding their credit, reduce reliance on existing credit, and refrain from applying for credit unless necessary.
Poor Credit Score
Individuals with poor credit scores fall into the high-risk category for lenders. The prospects of credit approval for this group are dim. Banks and financial institutions cautiously approach those with poor credit scores, as it indicates financial instability, excessive debt, or a history of missed payments. Even if a lender agrees to provide a loan, they may require a guarantor to mitigate the associated risks.
Conclusion
Regularly monitoring your CIBIL score lets you stay informed about your credit health. Checking credit reports allows you to identify inaccuracies and take corrective measures promptly. Several online platforms offer free access to your credit report, making it a convenient practice. Improving your CIBIL score involves adopting responsible financial habits. Timely payments, reducing outstanding debts, and maintaining a balanced credit mix positively affect your score. It's a gradual process that requires consistency and diligence.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.