Fincash » The Future of Money - Will Physical Cash Disappear
Table of Contents
The Future of Money – Will Physical Cash Disappear?
For youngsters and people living in urban, cash is becoming obsolete, they go on for months without seeing paper notes. For some cash is the only option. Let’s take a look at the future of money.
The digital transaction has shown robust growth after the 2016’s note bandi (note ban). In fact, we can say that demonetisation marked the beginning of the digital era. Moreover, the Digital India programme, a flagship programme of the Government of India, sets a vision to transform the country into a digitally empowered society and knowledge Economy. ‘Faceless, Paperless, Cashless’ is one of the professed roles of Digital India.

Not just this, the Pandemic was another wave toward cashless movements. It changed the way we use cash in brick-and-mortar stores. Online transactions gave room to social distance. Today people are able to make instant payments from anywhere around the world, which couldn’t have been possible with paper notes.
What about cash? If you view the situation from afar, it seems clear that cash is becoming obsolete. But, notes have been in circulation for several human lifetimes. We have historic portraits on notes which builds up an emotional touch and gives a notion of patriotism. Even though we are progressing super fast by adapting to the power of techno, a few old-school things won’t replace ever. For example, the Indian festive celebration is incomplete without the mandatory Shagun envelopes (cash gifts). Also when it comes to giving a tip to a food delivery person or a labourer, people still prefer giving loose cash from their wallets. Grandparents express their love towards their grandchildren by giving cash. A small donation at temples or to the Preist is given in cash. These are a few examples of many such special moments where cash is a medium of expressing love.
Apart from these emotions, cash is untraceable. If you want to buy something without anybody tracing you back, cash is the best way to do it. Liquid cash also acts as an emergency fund. In a place where the internet Range is weak or there is no network tower of a particular sim card, cash keeps you safe. Money note is also a medium of exchange among the poor.
The rise of electronic payments
Many retailers, cafes, restaurants, etc., aren’t taking cash anymore. Some online stores are turning away from Cash on Delivery (COD). Banks are adapting robust technology for seamless transactions and securing customers’ data. The physical and paperwork with the Bank have come online. People can open accounts, transfer money, pay online, book flights, pay insurance premiums, bills, etc. I remember back then, I used to leave home an hour early for my work if I had to stop by to pay the electricity bill. Today paying bills is at fingertips.
With over 560 million internet users, today, India is the second largest online Market in the world. As per reports, India accounted for 48 billion worldwide real-time transactions in 2021. Interestingly, 80% of transactions originate in tier 2, tier 3, and tier 4 cities and beyond.
Talk to our investment specialist
Game changer - Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
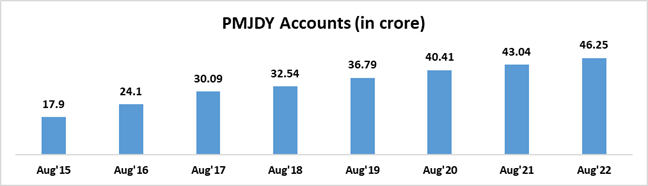
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), launched in 2014, has 46.40 Crore beneficiaries banked as of 6th Sept’22. Millions of the poor now have access to banks due to this scheme. As said by PM Modi - this initiative has been a game-changer, serving as the foundation for several poverty alleviation initiatives, benefitting crores of people. By this point, let’s assume that over the next few years, even poor people will start getting used to online payments. As the idea of the current BJP Govt is to give people digital literacy and push them towards savings, etc.
The risk of digital payment
But the other side of digital payment is also the growing number of theft and security issues. Fraudulent UPI handles, phishing scams, screen monitoring by fraudsters and unauthorised payment links are some of the potential risks in UPI payment. Even some businesses have experienced fake payments from customers due to which they are now accepting payments only in cash.
The Reserve Bank of India has many times flagged concerns over terror financing, money laundering, etc with private cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ether, etc. The RBI is working with various technological experts for improvising digital transactions and make them less risky as much as they can. On the other hand, it is also up to people how carefully they use the digital method of payment. Downloading authentic Apps, not declaring personal bank details, checking spam warnings on phone, etc are some of the things you have to be careful about.
There’s little doubt that the elimination of cash would enable banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions to reduce staff. After all, it takes more people to Handle the business of cash transactions. Electronic payment methods, by contrast, are completely digital. Far fewer people are needed to manage the process.
Final words
Both cash and digital payments have their own pros and cons. Back then carrying too much liquid cash could build the fear of mishandling or theft. While today making digital payments is easy, cyber security is becoming a concern. Though today cash is getting smaller, it has its own role to play. Thus, it will never go away.
 By Rohini Hiremath
By Rohini Hiremath
Rohini Hiremath works as a Content Head at Fincash.com. Her passion is to deliver financial knowledge to the masses in simple language. She has a strong background in start-ups and diverse content. Rohini is also an SEO expert and motivating team head!
You can connect with her at rohini.hiremath@fincash.com
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.