What is Operating Cash Flow Ratio?
The operating cash flow ratio, or cash flow coverage ratio, is a financial metric that measures a company's ability to generate cash from its operations to cover its Current Liabilities. It indicates how much cash a company generates from its operating activities compared to its short-term obligations. The higher the operating cash flow ratio, the better a company can meet its short-term financial obligations. This ratio is essential in analysing a company's liquidity and financial health.

Calculation of Calculating Operating Cash Flow Ratio
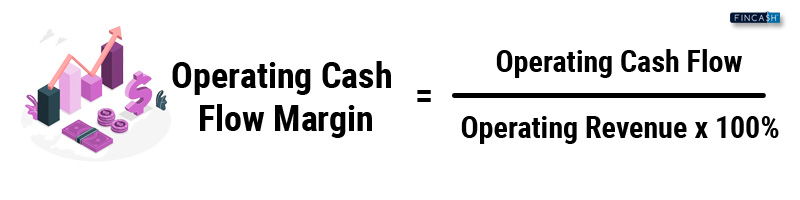
The formula to calculate the operating cash flow ratio is:
Operating Cash Flow Ratio = Operating Cash Flow / Current Liabilities
Where,
- Operating Cash Flow = Net Income + Non-Cash Expenses - Changes in Working Capital
- Current Liabilities = Short-term obligations due within a year, including accounts payable, current portion of long-term debt, and other current liabilities.
A company's cash flow statement will show operating cash flow, while current liabilities can be found on its Balance Sheet. Once you have these values, divide operating cash flow by current liabilities to obtain the operating cash flow ratio. The resulting ratio provides insights into a company's liquidity and ability to meet its short-term obligations.
Talk to our investment specialist
Factors That Affect Operating Cash Flow Ratio
A company's operating cash flow ratio is affected by several factors, which include as follow:
Industry: The operating cash flow ratio can vary significantly depending on the type of Industry a company operates in. Some industries require more working capital than others, leading to lower ratios.
Business Cycle: The Economic Cycle can affect the operating cash flow ratio. During a downturn, companies may face decreased sales and increased costs, leading to lower ratios.
Capital Expenditures: Heavy investments in Capital Expenditures, such as new equipment or buildings, can reduce a company's cash flow and impact its operating cash flow ratio.
Changes in Working Capital: Changes in a company's working capital, such as inventory levels, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, can impact its cash flow and operating cash flow ratio.
Revenue Growth: Rapid revenue growth can strain a company's cash flow and reduce its operating cash flow ratio.
Profit Margins: Lower profit margins can reduce a company's operating cash flow ratio, as it has less cash available to cover its short-term liabilities.
Pricing Strategies: A company's pricing strategy can impact its cash flow and operating cash flow ratio. For instance, discounting prices to increase sales may reduce cash flow in the short term.
Accounts Receivable and Payable Management: Efficient management of accounts receivable and payable can improve a company's cash flow and operating cash flow ratio.
Inventory Management: Effective inventory management can help reduce working capital and improve a company's operating cash flow ratio.
Seasonality: Companies with seasonal fluctuations in revenue may experience variations in their operating cash flow ratio throughout the year.
Acquisitions or Divestitures: Mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures can impact a company's cash flow and operating cash flow ratio.
Debt Repayments or Issuances: The repayment or issuance of debt can impact a company's cash flow and operating cash flow ratio, as it affects the amount of cash available to cover short-term obligations.
Significance of Operating Cash Flow Ratio
Here are some key benefits of using the operating cash flow ratio:
- The operating cash flow ratio helps investors and analysts assess a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations using its operating cash flow.
- A high operating cash flow ratio indicates a company has enough cash to cover its short-term obligations, suggesting it is in good financial health.
- The operating cash flow ratio can be used to compare the liquidity of different companies or to track a company's liquidity over time.
- The operating cash flow ratio provides investors with insights into a company's ability to generate cash from its operations, making it a crucial Factor in investment decisions.
- The operating cash flow ratio helps managers make informed decisions on working capital management, capital expenditures, and dividend payments.
Advantages and Limitations of Using the Operating Cash Flow Ratio
Here are some of the major advantages and disadvantages of the operating cash flow ratio:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Measures liquidity and financial health | Ignores non-operating cash inflows and outflows |
| Helps with investment and management decisions | It may not account for seasonality |
| Provides comparability | Varies by industry |
Final Thoughts
The operating cash flow ratio is an essential metric that provides insights into a company's liquidity and financial health. By measuring a company's ability to generate cash from its operations, the ratio can help investors, analysts, and managers make informed investment and management decisions. To conduct a more thorough study, it is crucial to be aware of the ratio's limits and combine it with other financial measures. Overall, the operating cash flow ratio is a critical tool in financial analysis and an important aspect of evaluating a company's Financial Performance and health.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.