
Table of Contents
Reinsurance
What is Reinsurance?
We have seen how normal Insurance companies work. They pool a large number of people sharing a common risk i.e. Risk Pooling. But it is interesting to know that even the insurance companies that sell you insurance buy an insurance. These insurance companies buy insurance to make sure that they are able to fulfil the obligations they have towards the customers. This process of an insurance company transferring their risk to another insurance company is called Reinsurance.
The company that transfers the risk is called the ceding company and the accepting company is called reinsurer. The reinsurer agrees to indemnify the cedent against complete or a part of a loss which the primary insurance company may bear under certain insurance policies that it has sold. In return, the cedent pays a premium to the reinsurer. Also, the ceding company discloses all the information needed by the reinsurer to assess, set price, and manage the risks covered under the reinsurance contract.
Let’s give you an example:
Mr Ram has a Life Insurance policy with an insurance company of INR 10 crore. The insurance company now wants to transfer, say 30% of the risk, to the reinsurer. Then, in the case of loss the ceding company now has to pay the whole sum assured to Mr Ram’s beneficiary and ask the 30% it earlier insured from the reinsurance company. Mr Ram or his beneficiary has no connection to the reinsurance company. The life insurance contract is between Mr Ram and the primary insurance company and thus, the company is bound to settle the complete claim asked by Mr Ram or the beneficiary. The contract between the ceding company and reinsuring company is separate.
Who Offers Reinsurance?
It is important to note that not all insurance companies that are in the business play reinsurer to other insurance companies. The Capital requirement to settle the ceding company’s claim is much higher.
In India, general insurance Company was the sole reinsurer for over four decades. But The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDA) has approved the first phase of license to ITI Reinsurance and thus has opened the Indian insurance Market to the private overseas sector.
IRDA has granted the initial approval – known as R1 regulatory parlance – to four global players in the reinsurance Industry. Munich Re and Hannover from Germany, Swiss Re from Switzerland and French reinsurance giant SCOR. There is an ongoing process of confirming the final licence i.e. R2 to these global reinsurers and may take some time. Munich Re is the largest reinsurance company in the world followed by Swiss Re and Hannover. The US-based Reinsurance Group of America (RGA) and UK-based XL Catlin have also applied for operating in the Indian market. For a regular insurance company, there are three stages of clearance but there are only two levels for reinsurance companies.
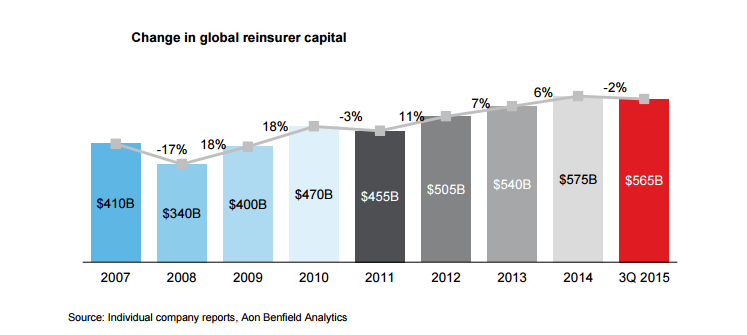
Who Buys Reinsurance?
We already know that primary insurance companies need reinsurance. But there are companies who specifically buy insurance to keep the business running. The reinsurers deal with the ceding companies, reinsurance intermediaries, multinational corporations and banks.
The business model of the primary insurance company decides how much of the business needs to be insured. The company also considers its capital muscle, risk appetite, and assess the current market conditions before buying the reinsurance.
Insurers whose portfolios are vastly exposed to natural or catastrophic disasters like flood, earthquakes, etc. need insurance cover the most. While small players that might need a bigger reinsurance cover because of the diversity of insurance risk coverage and large client base.
Companies with a focused line of working or with a specific clientele need more reinsurance cover than those with a diverse Range of clientele. In the case of commercial portfolios, even though the risk number is small (aviation industry or utility industry) the exposure is very large and thus such companies need more reinsurance cover.
In many cases, companies seek the insurance cover in order to benefit from the reinsuring company’s expertise and financing while the ceding company expands its product range or move into a new geographical area.
Types of Reinsurance:
There are two types Reinsurance:
Facultative Reinsurance
Facultative Reinsurance is the type of reinsurance which covers a single risk. It is considered to be more transaction-based. Facultative reinsurance allows the reinsurer to assess the individual risk and take a Call on whether to accept or reject it. The profit structure of the reinsuring company plays a part in deciding which risk to take. In such agreements, the ceding company and the reinsurer create a facultative certificate that states the reinsurer is accepting a specific risk. This type of reinsurance can be more expensive for the primary insurance companies.
Reinsurance Treaty
In this type, the reinsurer agrees to accept all of a specific type of risk from the primary insurance company. In treaty contract, the reinsuring company are bound to accept all the risks that are mentioned in the contract. There are two types of the treaty contract:
- Quota or Quota Share:
It is the consolidated type of risk-sharing The ceding company transfers some percentage of the risk to the reinsurer and keeps a certain percentage to itself. The percentage in fixed in the given contract.
- Surplus Insurance:
There are three aspects to look at:
- What is the maximum cover the reinsuring company is ready to accept?
- What is the maximum loss (sum assured for Life Insurance and indemnity assessed for General Insurance)?
- What is the percentage of risk to be transferred?
After calculating these factors, the treaty contract is proposed.
How Risks are Covered?
There are two ways in which reinsurer covers the risk in the given contract:
Risk of Excess Loss
The reinsurer proposes to give a certain amount as a cover to the ceding company if the loss occurs up to a specified amount. For eg. The reinsurance company agrees to pay INR 50,000 for a loss in excess of INR 1,00,000.
Aggregate Risk Excess of Loss
It is similar to the above-mentioned But here, the primary insurance company has to wait for all the claims in a year, sum all of it and if the calculation exceeds the cover promised by the reinsurer, then the promised amount will be covered.
Premiums In Reinsurance
There are again two types of paying a premium:
Original Premium or Direct Premium
If say 30% of the risk is transferred to the reinsurer then 30% of the premium received by the primary insurance company is directly transferred to the reinsurer.
Revised Risk Premium
The reinsuring company doesn’t care what the ceding company charges their client for premium. It states its own premium to the cedent for a certain risk to be covered.
Talk to our investment specialist
Benefits of Reinsurance
- Reduce the Volatility of results of underwriting.
- There is a flexibility in financing and there is also a capital relief.
- The ceding company can access the reinsuring company’s expertise and services especially in the fields of pricing, underwriting, product development, and claims
These benefits are applicable for both Life and Non-Life Insurance. However, due to different approaches of the primary insurance companies, the importance of these benefits may vary to different sectors.
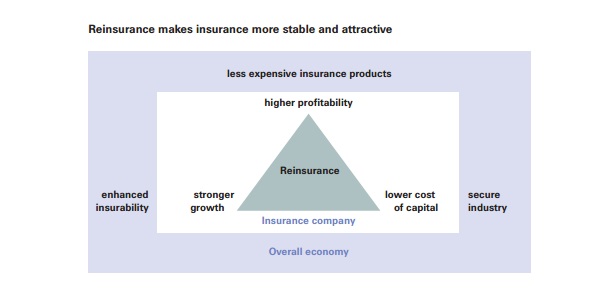
Conclusion
Reinsurance is one of the major capital and risk management tools available to the primary insurance industry. But it is rarely heard outside the insurance sector. Even the reinsuring companies have their own reinsurers called Retroinsurers. Reinsurers provide protection to the insurance industry for a diverse range of risks and also gives them capital relief. Reinsurance makes insurance sector more stable and attractive.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.







Yes it is useful
Getting something new