Table of Contents
The Five Cs of Credit Explained
The five primary variables used to assess a potential borrower's creditworthiness are referred to as the 5 Cs of Credit. The algorithm considers five borrower attributes as well as loan terms in order to predict the likelihood of Default and, as a result, the risk of financial loss to the lender.

What are these five Cs, though? Character, capacity, Capital, Collateral, and conditions are the five Cs of credit.
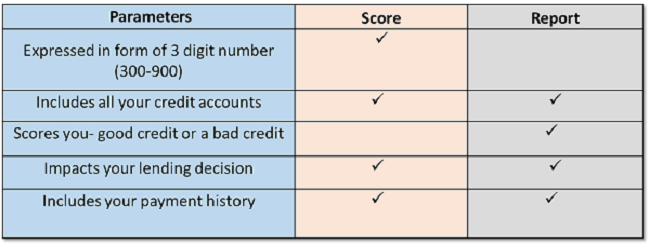
Credit ratings are used by financial organisations to measure and assess if an applicant is creditworthy, as well as to set interest rates and credit limitations for current customers. A Credit Report details the borrower's overall debt, current amounts, credit limitations, and any defaults or bankruptcies that have occurred in the past.
Understanding the Five Cs of Credit
Knowing the five Cs can help one position oneself as a possible borrower to lenders. Let's have a look into what each of these terms entails and how one can prepare his/her company.
Character in 5Cs of Credit
The most extensive component of creditworthiness assessment is character. The rationale behind is that a person's credit and payment history reveal their character to a lender, that is their proclivity for timely repayment of a loan. Defaults in the past suggest carelessness or irresponsibility, both of which are negative personality qualities. A lender will check the personal credit of all borrowers and guarantors engaged in the loan, keeping in mind that the past is the best predictor of the future.
Talk to our investment specialist
Capacity in 5Cs of Credit
The capacity of a borrower to pay back the loan is an important aspect in evaluating the lender's risk exposure. Income, employment history, and current job stability all Factor towards one's capacity to repay existing debt. Other responsibilities like college fees payment, treatments for old people and so on are also taken into account when determining one's future financial obligations. The Debt-to-Income Ratio of an organisation, which is the ratio of its current debt to current income (before Taxes), may be assessed to check the capacity of the borrower.
Capital in 5Cs of Credit
The amount of assets held in the borrower's name is referred to as capital. It reflects one's money, investments, and assets like Land, jewels, and so forth. Loans are repaid largely with household income; capital provides extra security in the event of unanticipated events or setbacks, such as unemployment.
Conditions in 5Cs of Credit
The terms of any credit transaction, such as the principal amount or interest rate, are referred to as conditions. Lenders evaluate risk depending on how the borrower intends to utilise the funds if they are awarded. Other external factors are taken into account, such as the health of the Economy, current federal interest rates, Industry-specific legislation, and political change.
Collateral in 5Cs of Credit
Borrowers must pledge specific assets under their names as collateral when applying for a secured product such as a vehicle loan or a house loan. Fixed assets, such as a land agreement, as well as Financial Assets and securities, such as Bonds, are examples of collateral. By subtracting the value of existing debts secured by the same asset, the value of the collateral is determined. The residual equity represents the real worth of the borrower's collateral. The type of asset, its location, and prospective marketability all have a role in determining the liquidity of collateral.
The Bottom Line
Although each financial institution has its own technique for determining a borrower's creditworthiness, these components are often used for both personal and commercial credit applications. The borrower's capacity to produce cash flow to cover the interest and principal on the loan is typically seen as the most significant of the five. Applicants who score well in each category, on the other hand, are more likely to get huge loans, cheaper interest rates, and more advantageous payback conditions.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.