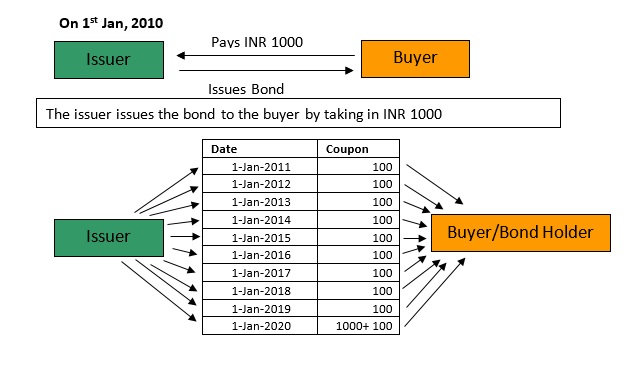
Table of Contents
What is the Emerging Markets Bond Index?
The Emerging Markets Bond Index is a Market index covering the performance of Bonds issued by emerging countries. The index was created in 1995 by J.P. Morgan, HSBC, BNP Paribas, Standard & Poor's and other banks, currently comprising 21 countries. Countries that no longer meet the index's listing criteria or have suspended their secondary market trading are removed.
The Emerging Markets Bond Index (EMBI) consists of publicly issued debt securities and currently comprises almost 800 bonds from 20 emerging markets.
How does the EMBI Work?
The EMBI measures the global economic power balance. It calculates each country's development by dividing GDP by population. This is called the "EMBI ratio", which calculates how economically powerful a country is relative to its size and population.
Emerging Markets Opportunities
Emerging markets offer the opportunity for companies to compete on a global stage and give them access to diverse cultures and customers. They are still growing, which means there are a lot of opportunities in the future. This is a chance to dominate the market before it becomes saturated. There are also fewer competitors, which make emerging markets an easier place to make money.
Talk to our investment specialist
Benefits of Investing in EMBI
Investing in EMBI is an excellent idea as it offers a lot of benefits to investors, such as:
- It is the only investment instrument that offers high returns and low risk.
- It provides an opportunity to diversify your Portfolio as it has a low correlation with other asset classes like equities and bonds.
- The market for this product is under-penetrated and presents a significant growth potential.
- It does not attract withholding tax and other Taxes on Income and Capital gains and has no lock-in period.
- Investing in EMBI can be a great way to earn money through dividends, capital appreciation, and the various tax benefits associated with it.
Market Outlook for EMBI
The economic outlook for EMBI depends on various factors such as Inflation, Economic Growth rates, government interest rates, and foreign exchange rates, among others. The bond market is a Fixed Income market that deals with debt instruments that have grown to $100 trillion since its inception.
Today the EMBI consists of over 250 outstanding bonds from 35 countries. These include Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, Turkey, India and China. By focusing on emerging markets instead of developed ones, EMBI can provide investors with additional yield over similarly developed market bonds while also providing higher growth potential due to faster economic growth rates found in emerging markets.
Emerging Market Bonds - Current Issues
The bond market is currently facing several challenges. One of the main is the proliferation of bond ETFs and other passive instruments that have increased competition for traditional players in the market. Another challenge facing the market is the declining liquidity in the secondary markets and raised transparency and reporting standards.
Emerging Markets Bond Index Currency
- The EMBI is made up of the Emerging Market Currencies (EMC), which are the following:
- BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa)
- Next 11 (Bangladesh, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Mexico, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Turkey, South Korea and Vietnam)
- Others (including frontier markets such as Colombia and Ukraine)
- These countries' stock markets are under ten years old, making them emerging. Compared to other developed countries, they have high growth potential.
Emerging Markets Risks
Investing in emerging markets has the potential to yield significant returns, but it is not without risk. There are two significant risks - the first being the maturity of your competitors. If your competitors outperform your emerging markets, you may be competing both globally and locally. The other risk is that while these markets are generally growing at high rates, they can also fall into crisis or slow down.
Emerging Markets Bond Index Vs Individual Securities
Investing in a Mutual Fund or index is a great way to diversify your portfolio. When you buy an index, you buy a slice of the whole market rather than picking individual stocks.
An EMBI is a fund of funds. When you invest in an EMBI, you are indirectly investing in the Underlying investments of the EMBI. Individual security is a stock that you buy or sell on its own without it being part of any other investment product.
Conclusion
The EMBI is a one-of-a-kind index concerning measuring the behaviour of emerging markets. It can measure changes in capital flows, trade, and interest rates for the different economies involved in the index. This helps investors understand how risks may be associated with investing in certain countries or sectors within those countries. Emerging Markets stocks are increasingly becoming the focus of active investors, who believe they offer better opportunities for growth than developed economies.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.