
Table of Contents
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDA)
IRDA stands for insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India. It is an autonomous and the statutory body tasked with regulating and promoting insurance and reinsurance in the country.

IRDA was constituted by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act - IRDA Act, 1999 and has its headquarters in Hyderabad, Telangana. In the recent times, IRDA has moved on to a more digital platform to help and cater the needs of both the Insurance companies, agents and policyholders. Every year IRDA online exam is conducted and the exam results are displayed on the IRDA website.
New: IRDAI announces guidelines for COVID-19 health policies under Corona Rakshak Policy and Corona Kavach Policy. These are the standard health policy which will be offered on indemnity Basis.
| IRDA | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India |
| Chairman, IRDAI | Subhash Chandra Khuntia |
| IRDA Grievance Call Centre | 1800 4254 732 |
| complaints[at]irda[dot]gov[dot]in | |
| Head Office | Hyderabad |
| Hyderabad Office Contacts | Ph:(040)20204000, e-mail: irda[@]irda.gov.in |
| Delhi Office Contacts | Ph:(011)2344 4400, e-mail: irdandro[@]irda.gov.in |
| Mumbai Office Contacts | Ph:(022)22898600, e-mail: irdamro[@]irda.gov.in |
Brief History of Insurance in India
Insurance in India dates back to the 19th Century with the establishment of Oriental Life Insurance Company in Kolkata in 1818. The Indian Life Insurance Assurance Companies Act of 1912 was the first law that regulated life insurance in the country. Life Insurance Corporation was established in the year 1956 with the nationalisation of the life insurance sector. The LIC absorbed then currently functioning 154 Indian and 16 non-Indian insurers and 75 provident societies. LIC enjoyed a complete monopoly till the late 1990s when the insurance sector was opened to the private sector
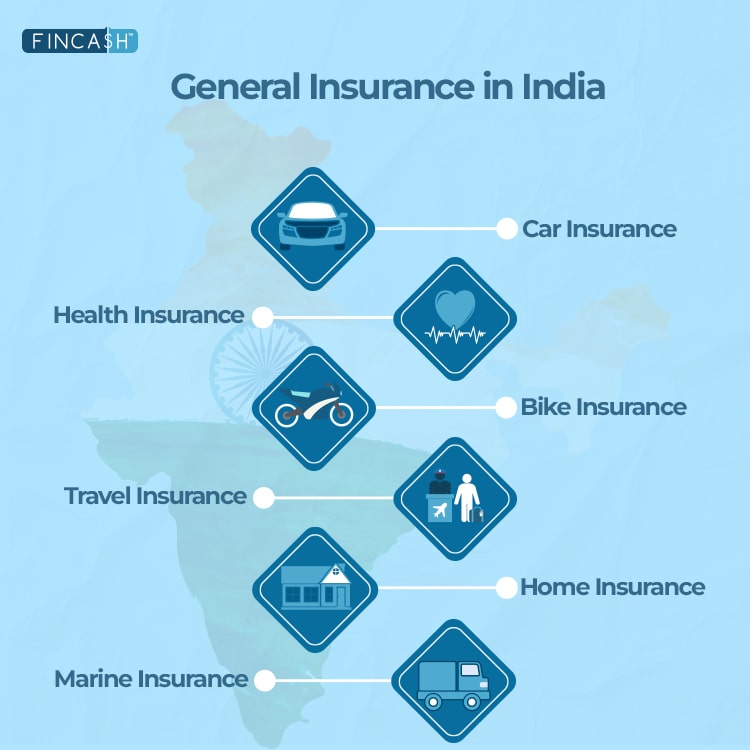
general insurance in India, on the other hand, began during the Industrial Revolution with the establishment of Triton Insurance Company in Kolkata in 1850. In the year 1907, the Indian Mercantile Insurance was formed. It was the first company to underwrite all the classes of general insurance. In 1957, a wing of Insurance Association of India – General Insurance Council – was established to frame the code of conduct and regulate the means of fair business practices. The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act was passed in 1972 and the insurance Industry was nationalised on January 1st 1973. A hundred and seven insurers were amalgamated and formed a group of four insurance companies – National Insurance Company, New India Assurance Company, Oriental Insurance Company and United India Insurance Company. The General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re) was established in 1971 and was effective on January 1st 1973.
By the year 1991, the Government of India began to plan the economic reforms in the insurance sector. For the purpose, a committee was formed in 1993 for the reforms in the insurance sector. The committee was headed by Shri R. N. Malhotra (Retired Governor of the Reserve Bank of India). The Malhotra Committee recommended some major reforms in the insurance sector such as allowing private sector companies to promote insurance in the country, allowing foreign promoters in the domestic insurance Market and formation of an independent regulatory body answerable to Parliament and the Government.
An interim body called Insurance Regulatory Authority was set up in 1996. In the year 1999 Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) Act was passed and on April 19th 2000, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) of India received autonomous status.
Structure of IRDA
IRDA is a ten-member body that consists of:
One Chairman (for five years and maximum age of 60 years) Five whole-time members (for five years and maximum age of 62 years) Four part-time members (not more than five years) The chairman and the members of IRDA are appointed by the Government of India.
Current Chairman of IRDA is Mr Subhash Chandra Khuntia.
Objectives of IRDA
To promote the interests and rights of the policyholders. To promote and monitor the growth of the insurance industry. To prevent frauds and misselling of insurance product and ensure speedy settlement of genuine claims To bring transparency and proper code of conduct in financial markets dealing with insurance.
Functions and Duties of IRDA:
According to Section 14 of IRDA Act of 1999, the agency has the following functions and duties:
- Issuing the registration certificates to insurance companies and regulate them
- Protect the interests of the policyholders
- Provide licences to insurance intermediaries like agents and brokers after stating the required qualifications and set guidelines for their code of conduct
- Promote and regulate professional organisations related to insurance to enhance the development of the sector
- Regulate and supervise the premium rates and terms of the insurance policies
- Specify the conditions and manners by which the insurance companies have to present their financial reports
- Regulate the investment of the policyholders’ funds by the insurance companies.
- Ensure the maintenance of the solvency margin i.e. the ability of an insurance company to pay out claims.
Talk to our investment specialist
Insurance Repository
The Finance Minister of India announced an insurance repository system, helping policyholders buy and maintain insurance policies in electronic form rather than on paper. Insurance repositories, like share depositories or Mutual Fund transfer agencies, will hold electronic records of insurance policies issued to individuals as electronic or e-policies.
IRDA Portal
The agency has its online portal to help customers and agents online. IRDA lists its regulations, exam information and other important information on the online portal.
There are some important things to note on the IRDA portal:
- There is no such thing as IRDA insurance. The agency does not sell insurance; it is a regulatory body.
- www. irdaonline.org is the website to access the agency information online.
- It is mandatory to register on IRDA agent portal in order to appear for the online exam.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.
You Might Also Like











Very helpful information irda in insurance
Very good
HelpFull to teach My agents