What are Exchange Traded Funds or ETFs?
An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment that is bought and sold on stock exchanges. The ETF trade is similar to the trade in stocks. ETFs can have underlying assets like commodities, Bonds, or stocks.

An exchange traded fund is like a Mutual Fund, but unlike a Mutual Fund, ETFs can be sold at any time during the trading period.
After the introduction of Mutual Funds, exchange traded funds have become an innovative and popular means to invest in the market. Here we will learn about different types of ETFs in India like Index Funds ETF, gold ETF, Bond ETF, etc., also we will show benefits of investing in ETFs, Risks Under ETF Funds, Best ETFs to invest along with a comparison of exchange traded funds Vs Mutual Funds.
What Does an ETF Contain?
ETFs can contain stocks, bonds, commodities, foreign currency, money market instruments, or any other security. An exchange traded funds may also contain an index like the S & P 500 (United States), Nifty 50 (India) or any other index/benchmark of any country. An ETF could also contain derivative instruments.
Types of Exchange Traded Funds (ETF)
There are various types of exchange traded funds with each having different underlying components.
Index Funds ETF
An Index ETF is mainly a passive Mutual Fund that allows investors to purchase a pool of securities in a single transaction. The objective here is to track the performance of a stock market index (for e.g. Nifty 50). When an investor purchases a quantity of an index fund or ETF, it means that the investor is purchasing a share of a Portfolio that contains the securities of the underlying index. Some of the popular Index ETFs in India are HDFC Index Fund-Nifty, IDFC Nifty Fund, etc.
Fund Selection Methodology used to find 5 funds
Gold ETF
Gold ETFs are instruments that are based on gold prices or invest in gold bullion. Gold exchange-traded funds track the Gold bullion performance. When the gold price moves up, the value of the exchange-traded fund also rises and when the gold price goes down, the ETF loses its value. In India, Reliance ETF Gold BeES is a listed exchange traded fund along with other ETFs. There are mutual funds that also allow investors to take exposure to exchange-traded funds in gold. Some of the best performing underlying gold ETFs having AUM/Net Assets > 25 Crore to invest are:
Fund NAV Net Assets (Cr) 3 MO (%) 6 MO (%) 1 YR (%) 3 YR (%) 5 YR (%) 2024 (%) Aditya Birla Sun Life Gold Fund Growth ₹41.2433
↑ 0.48 ₹1,136 11.7 44 79.6 34.1 22.1 72 Invesco India Gold Fund Growth ₹39.8294
↓ -0.11 ₹302 12.3 42.6 76.2 34 21.5 69.6 SBI Gold Fund Growth ₹41.687
↑ 0.64 ₹9,324 12.5 44.2 78.8 34.7 22.4 71.5 Nippon India Gold Savings Fund Growth ₹54.382
↑ 0.76 ₹4,849 12.2 43.8 78 34.3 22.1 71.2 HDFC Gold Fund Growth ₹42.586
↑ 0.63 ₹7,633 12.5 44 78.7 34.2 22.2 71.3 Note: Returns up to 1 year are on absolute basis & more than 1 year are on CAGR basis. as on 14 Jan 26 Research Highlights & Commentary of 5 Funds showcased
Commentary Aditya Birla Sun Life Gold Fund Invesco India Gold Fund SBI Gold Fund Nippon India Gold Savings Fund HDFC Gold Fund Point 1 Bottom quartile AUM (₹1,136 Cr). Bottom quartile AUM (₹302 Cr). Highest AUM (₹9,324 Cr). Lower mid AUM (₹4,849 Cr). Upper mid AUM (₹7,633 Cr). Point 2 Established history (13+ yrs). Oldest track record among peers (14 yrs). Established history (14+ yrs). Established history (14+ yrs). Established history (14+ yrs). Point 3 Top rated. Rating: 3★ (upper mid). Rating: 2★ (lower mid). Rating: 2★ (bottom quartile). Rating: 1★ (bottom quartile). Point 4 Risk profile: Moderately High. Risk profile: Moderately High. Risk profile: Moderately High. Risk profile: Moderately High. Risk profile: Moderately High. Point 5 5Y return: 22.11% (lower mid). 5Y return: 21.51% (bottom quartile). 5Y return: 22.37% (top quartile). 5Y return: 22.09% (bottom quartile). 5Y return: 22.19% (upper mid). Point 6 3Y return: 34.05% (bottom quartile). 3Y return: 33.98% (bottom quartile). 3Y return: 34.68% (top quartile). 3Y return: 34.27% (upper mid). 3Y return: 34.22% (lower mid). Point 7 1Y return: 79.63% (top quartile). 1Y return: 76.17% (bottom quartile). 1Y return: 78.77% (upper mid). 1Y return: 78.02% (bottom quartile). 1Y return: 78.68% (lower mid). Point 8 1M return: 7.79% (lower mid). 1M return: 7.17% (bottom quartile). 1M return: 8.00% (top quartile). 1M return: 7.63% (bottom quartile). 1M return: 7.99% (upper mid). Point 9 Alpha: 0.00 (top quartile). Alpha: 0.00 (upper mid). Alpha: 0.00 (lower mid). Alpha: 0.00 (bottom quartile). Alpha: 0.00 (bottom quartile). Point 10 Sharpe: 3.57 (upper mid). Sharpe: 3.52 (bottom quartile). Sharpe: 3.54 (lower mid). Sharpe: 3.61 (top quartile). Sharpe: 3.54 (bottom quartile). Aditya Birla Sun Life Gold Fund
Invesco India Gold Fund
SBI Gold Fund
Nippon India Gold Savings Fund
HDFC Gold Fund
Leveraged ETF
Leveraged ETFs use derivatives or debt to boost the potential returns on an underlying index. It is considered to be suitable for a short-term investment, but such exchange traded funds are currently not available in India.
Bond ETF
The Bond ETF is very similar to bond mutual funds. Bond exchange traded funds are a portfolio of bonds that trade on an exchange like a stock and they may be passively managed. LIC Nomura MF G-Sec Long Term ETF and SBI ETF 10 year Gilt are some of the bond ETFs available in India.
Sector ETF
The Sector exchange traded fund invests solely in stocks and securities from a specific sector or industry. Some of the sector-specific ETFs are Pharma funds, Technology funds, etc having an underlying in these specific sectors. Some sector ETFs currently in India are RShares Dividend Opportunities ETF, RShares Consumption ETF, Reliance Infra BeES, MOSt Shares M100, SBI ETF Nifty Junior, Kotak PSU Bank ETF to name a few.
Currency ETF
Currency exchange traded funds allow the investor to participate in currency markets without buying a specific currency. This is invested either in a single currency or in a pool of currencies. The idea behind this investment is to track the price movements of a currency or a basket of currencies.
Talk to our investment specialist
Exchange Traded Funds in India
The history of ETFs in India is relatively short with ETFs having been introduced in 2001. The first ETF to be launch in India was Nifty BeES launched by Benchmark Asset Management Company ( Benchmark AMC was acquired by Goldman AMC, which was recently also acquired by Reliance AMC). Thereafter a number of ETFs have come into India, however, exposures are possible only in a very limited number of areas such as Nifty, certain mid-cap indices and sector indices in equity. Commodity would be predominantly gold, and in bonds, there are hardly any ETFs available; Liquid Bees (similar to Liquid Funds) and LIC Nomura MF G-Sec Long Term ETF (G-sec based ETF) to name a few.
Globally, exchange traded funds started in 1989 in the United States with the S & P 500 being the first index to be converted into an ETF. Thereafter, many ETFs have come into the markets globally and today ETF assets globally have exceeded $ 3 trillion.
Given where we are the ETF space it would take some time before enough Investing options become available to investors to create meaningful portfolios. However, for certain basic exposures like Nifty one can look to invest.
ETFs Investing: Benefits
Some of the benefits of investing in exchange traded funds are as follows-
- Low cost- ETFs make an affordable investment due to their lower expense ratios than a Mutual Fund.
- Tax Advantage- The reason why exchange traded funds are very tax efficient is that the buying and selling of shares in the open market doesn't impact an exchange-traded fund’s tax obligation.
- Liquidity- Exchange traded funds can be sold and bought at any time throughout the trading period.
- Transparency- There is a high level of transparency in ETFs as the investment holdings are published every day.
- Exposure- Exchange traded funds provide diverse exposure to a specific sector as the case may be.
Exchange Traded Funds Vs Mutual Funds
When it comes to buying a pool of stocks, investors often get confused between Mutual Funds and exchange traded funds. Hence we will look at some of the major differences between Mutual Funds and ETFs.
Investing Process
- ETF: You can buy an ETF from an online Trading Account. This is similar to buying stocks.
- Mutual Fund: Here you don’t need an online trading account. Investors can invest in Mutual Funds through the AMC (directly), via a broker, an advisor or a trading account.
Liquidity
- ETF: You can buy or sell an ETF at any time during the trading session.
- Mutual Fund: When you sell the units of a Mutual Fund, depending on the type of fund it may take a few days to get your money creditedYou may have to pay exit load charges on early exits.
Charges
- ETF: The brokerage and delivery charges would be around 0.6% (of invested amount) and the expense ratio would be up to 1% p.a. of transaction value which may vary fund to fund.
- Mutual Fund: Mutual Fund’s expense ratio ranges from 1-3% p.a. and they also have an entry or exit charges which may range from 2-5% of invested amount.
Minimum Investment
- ETF: Under this investment, you can buy as little as one unit.
- Mutual Fund: There is a certain minimum amount to invest in Mutual Fund. For instance, if you invest through SIP, you have to invest at least INR 500 pm.
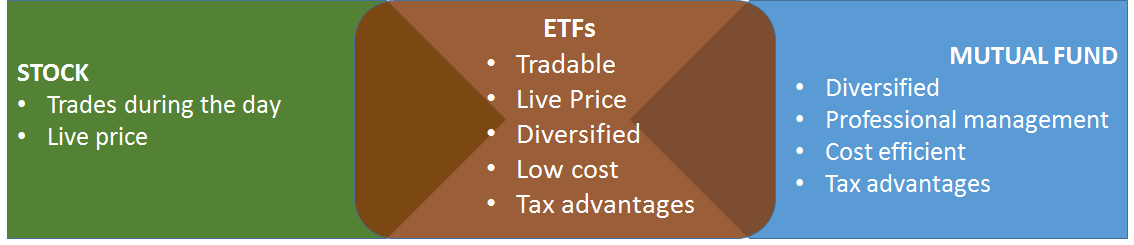
ETF Stock: Understanding Stocks ETFs
A stock ETF is traded just as a normal share of stock is traded on an exchange. A stock ETF also allows one to gain exposure to a basket of equities without having to purchase each individual security. In stock ETF, unlike a Mutual Fund, its price is adjusted throughout the trading session rather than at the market close. A stock ETF carries a certain type of expense like management fees, etc., but is typically lower than that of Mutual Funds.
How to Choose a Good ETF?
When trying to replicate an Index there is a measure called the tracking error, which measures how much the ETF deviates in returns from the index it is tracking. The lower the tracking error the better the index ETF. Else, one would need to see the objective of the ETF and the performance over time if it's not tracking an index.
Top ETFs
Top performing ETFs in India are as follows-
| Index ETFs | Gold ETFs | Sector ETFs | Bond ETFs | Currency ETFs | Global Index ETFs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reliance Nifty BeES | Reliance Gold BeES | Relaince Bank BeES | Reliance Liquid BeES | Wisdom Tree Indian Rupee Strategy Fund | Reliance Hang Seng BeES |
| ICICI Prudential Nifty ETF | Reliance Gold ETF | Kotak Banking ETF | SBI ETF 10 year Gilt | Market Vectors- Indian Rupee/USD ETN | MOSt Shares NASDAQ 100 |
| MOSt Shares M50 | Birla Sun Life Gold ETF | R* Shares Banking ETF | LIC Nomura MF G-Sec Long Term ETF | _ | _ |
ETF: List of Exchange Traded Funds in India
This is the list of exchange traded funds or ETFs in India-
| Name | Underlying Asset | Launch Date |
|---|---|---|
| Axis Gold ETF | Gold | 10-Nov-10 |
| Birla Sun Life Nifty ETF | Nifty 50 Index | 21-Jul-11 |
| CPSE ETF | Nifty CPSE Index | 28-Mar-14 |
| Edelweiss Exchange Traded Scheme – Nifty | Nifty 50 Index | 8-May-15 |
| Reliance Bank BeES | Nifty Bank | 27-May-04 |
| Reliance Infra BeES | Nifty Infrastructure | 29-Sep-10 |
| Reliance Junior BeES | Nifty Nex 50 | 21-Feb-03 |
| Reliance Nifty BeES | Nifty 50 Index | 28-Dec-01 |
| Reliance PSU Bank BeES | Nifty PSU BANK | 25-Oct-07 |
| Reliance Shariah BeES | Nifty50 Shariah Index | 18-Mar-09 |
| HDFC Gold ETF | Gold | 13-Aug-10 |
| ICICI Prudential CNX 100 ETF | Nifty 100 | 20-Aug-13 |
| ICICI Prudential Nifty ETF | Nifty 50 Index | 20-Mar-13 |
| ICICI Sensex Prudential Exchange Traded Fund | S&P BSE Sensex | 10-Jan-03 |
| Kotak Banking ETF | Nity Bank | 4-Dec-14 |
| Kotak Gold ETF | Gold | 27-Jul-07 |
| Kotak Nifty ETF Nifty | 50 Index | 2-Feb-10 |
| Kotak PSU Bank ETF | Nifty PSU BANK | 8-Nov-07 |
| MOSt Shares M100 | Nifty Midcap 100 | 31-Jan-11 |
| MOSt Shares M50 | Nifty 50 Index | 28-Jul-10 |
| Motilal Oswal MOSt Shares NASDAQ-100 ETF | Nasdaq 100 | 29-Mar-11 |
| Quantum Index Fund – Growth | Nifty 50 Index | 10-Jul-08 |
| R * Shares Banking ETF | Nifty Bank | 24-Jun-08 |
| R* Shares CNX 100 ETF | Nifty 100 | 22-Mar-13 |
| R* Shares Consumption ETF | Nifty India Consumption | 10-Apr-14 |
| R* Shares Dividend Opportunities ETF | Nifty Dividend Opportunities 50 | 15-Apr-14 |
| R* Shares Nifty ETF | Nifty 50 Index | 22-Nov-13 |
| R* Shares NV20 ETF | Nifty50 Value 20 Index | 18-Jun-15 |
| Reliance ETF Gold BeES | Gold | 8-Mar-07 |
| Religare Invesco Nifty ETF | Nifty 50 Index | 13-Jun-11 |
| SBI ETF Banking | Nifty Bank | 20-Mar-15 |
| SBI ETF Nifty | Nifty 50 Index | 23-Jul-15 |
| SBI ETF Nifty Junior | Nifty Nex 50 | 20-Mar-15 |
| SBI Gold ETF | Gold | 28-Apr-09 |
| UTI Gold ETF | Gold | 12-Mar-07 |
| UTI Nifty ETF | Nifty 50 Index | 3-Sep-15 |
| UTI Sensex ETF | S&P BSE Sensex | 3-Sep-15 |
Source: NSE and BSE India
Risks Under ETF Funds
Although exchange traded funds offer diverse choices and benefits over traditional Mutual Funds (mainly lower cost), one should know the risks involved in ETFs. Since, ETFs have an underlying which could be equities, bonds or commodities, there are risks associated with ETFs of the underlying asset. To name a few; tracking error (the difference in the value of the actual index and the underlying ETF), market risk of the underlying instrument are a few distinct risks involved in exchange traded funds that you need to be aware of before jumping into any investment.
Therefore, like with any investment, exchange traded funds comes with its own set of pros and cons. Investors should carefully weigh their Investment plan & goals and accordingly, decide the next steps. While investing in an ETF make sure you choose best-performing ETFs in India.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.
You Might Also Like