Table of Contents
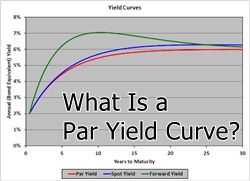
Defining Flat Yield Curve
A Flat yield curve is one in which the difference between short- and long-term rates for Bonds of similar credit grades is minimal. During transitions between normal and inverted curves, this form of yield curve flattening is common.
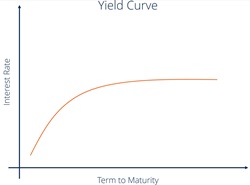
The difference between a flat yield curve and an average yield curve is that the former slopes upward while the latter does not.
Briefly Understanding Flat Yield Curve
When short and long-term bonds give equal yields, there is usually a minimal advantage to holding the longer-term instrument; the investor receives little additional compensation for the risks of keeping longer-term securities. The yield spread between long and short-term bonds is shrinking if the yield curve is flattening.
Long-term interest rates may be falling faster than short-term rates, or short-term rates may be rising more quickly than long-term rates, resulting in a flattening yield curve. As a result, investors and traders are usually concerned about the macroeconomic outlook when the yield curve is flat.
Flat Yield Curve Usage
A flat yield curve can signal a variety of factors outside a Recession. Market dynamics are generally efficient; nevertheless,
An artificial increase in short-term rates can often have an impact on the yield curve, flattening it. A flattening yield curve may be a warning sign for investors that we are entering a recession. As a result, investors should be cautious when evaluating a yield curve and regard it as simply one indicator of market circumstances.
Talk to our investment specialist
Flat Yield Curve as an Indicator for Lenders
A flat yield curve could signal lenders that we are about to enter a period of lower Inflation expectations. It is because long-term investors and lenders seek the yield on their investments to compensate for the effect of inflation. When a yield curve has flattened, and inflation is predicted to be lower, however, investors will be less concerned about inflation's impact and more concerned with the Opportunity Cost of a long-term investment.
Simply put, when there is a flat yield curve, investors receive the same amount of money for short-term and long-term investments. As a result, they can have a variety of market impacts, such as lowering long-term investments due to no net gain over short-term investments. In such a market, many investors will prefer short-term bonds to long-term bonds since they avoid the hazards of tying up their money in a long-term bond with the same profit and upside potential.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.