Table of Contents
Current Yield
What is the Current Yield?
Current yield is an investment's annual Income (interest or dividends) divided by the current price of the security. This measure looks at the current price of a bond instead of its Face Value. Current yield represents the return an investor would expect if the owner purchased the bond and held it for a year, but current yield is not the actual return an investor receives if he holds a bond until maturity.
Formula for calculating current yield.
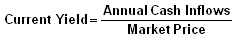
Details of Current Yield
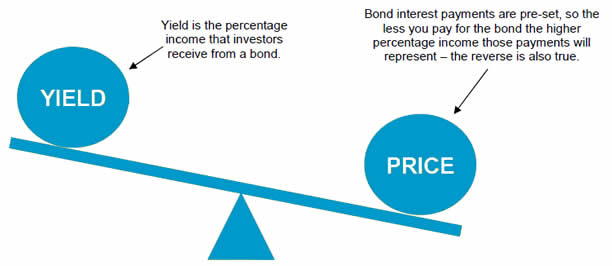
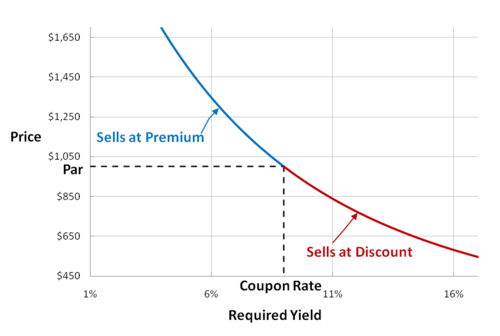
Current yield is most often applied to bond investments, which are securities that are issued to an investor at a par value (face amount) of Rs. 1,000. A bond carries a coupon amount of interest that is stated on the face of the bond certificate, and Bonds are traded between investors. Since the Market price of a bond changes, an investor may purchase a bond at a discount (less than Par value) or a premium (more than par value), and the purchase price of a bond affects the current yield.
How Current Yield Is Calculated
If an investor buys a 6% coupon rate bond for a discount of Rs. 900, the investor earns annual interest income of (Rs. 1,000 X 6%), or Rs. 60. The current yield is (Rs. 60) / (Rs. 900), or 6.67%. The Rs. 60 in annual interest is fixed, regardless of the price paid for the bond. If, on the other hand, an investor purchases a bond at a premium of Rs. 1,100, the current yield is (Rs. 60) / (Rs. 1,100), or 5.45%. The investor paid more for the premium bond that pays the same dollar amount of interest, so the current yield is lower.
Current yield can also be calculated for stocks by taking the dividends received for a stock and dividing the amount by the stock’s current market price.
Talk to our investment specialist
Factoring in Yield to Maturity
Yield to maturity (ytm) is the Total Return earned on a bond, assuming that the bond owner holds the bond until the maturity date. Assume, for example, that the 6% coupon rate bond purchased for a discount of Rs. 900 matures in the 10 years. To calculate YTM, an investor needs to make an assumption about a discount rate, so that the future principal and interest payments are discounted to present value.
In this example, the investor receives Rs. 60 in annual interest payments for 10 years. At maturity in 10 years, the owner receives the par value of Rs. 1,000, and the investor recognizes a Rs. 100 Capital Gain. The present value of the interest payments and the Capital gain are added to compute the bond's YTM. If the bond is purchased at a premium, the YTM calculation includes a Capital Loss when the bond matures at par value.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.