
Table of Contents
- Repo Rate Meaning
- Components of a Repo Transaction
- How is the Repo Rate Important?
- How RBI Calculates the Repo Rate?
- Impact of Repo Rate on a Common Man
- Relationship Between Inflation and Repo Rate
- Impact of Repo Rate on Home Loan
- Impact of Repo Rate on Fixed Deposits (FDs)
- Impact of Repo Rate on the Stock Market
- Similarities and Dissimilarities Between Bank Rate and Repo Rate
- Difference Between Repo Rate and Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate
- Wrapping Up
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Everything about Repo Rate
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced on April 6, 2023, that it will maintain the current repo rate, which is 6.5%. However, this decision was quite unexpected and brought a wave of surprise for several Market experts who predicted a hike. Over the last 11 months, the RBI increased this rate by 2.5%. But, this decision might be disappointing, especially for those with fixed deposits, as they were hoping for a hike to boost returns.
Despite this tumultuous decision, a section of people are still unaware of the entire concept of repo rate. If you are one of them, you are on the right path. This post covers a comprehensive guide to repo rates and everything you must know to understand this concept. Let’s get started.
Latest Update 2024:
- RBI Monetary policy: keeps repo rate steady at 6.5%, FY24 Inflation forecast at 5.4%
Repo Rate Meaning
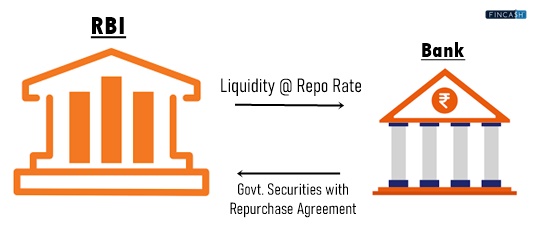
Repo rate is abbreviated for repurchase rate. It is the rate at which Indian commercial banks borrow money from the RBI. In this transaction, the RBI purchases securities, like government Bonds, from commercial banks with an agreement to sell them later, generally the following day or in another few days, at a higher price. The repo rate is the interest rate the RBI charges the banks for this loan.
The central bank uses the repo rate as an essential tool to regulate the money supply in the country. The central bank can impact the economic activity level by increasing or decreasing the repo rate, which impacts the borrowing and lending of commercial banks. If the repo rate is high, borrowing money is expensive for banks, leading to a decrease in lending and a downtrend in economic activity. On the other hand, a lower repo rate encourages banks to borrow money and kindle Economic Growth.
Components of a Repo Transaction
Here are some parameters considered by the RBI when executing the transaction with commercial banks:
Averting Economy Squeezes: The RBI decreases or increases the repo rate based on inflation. Hence, it objectifies regulating the Economy by limiting inflation
Liquidity or Cash Reserve: Banks borrow from the central bank to maintain cash reserve or liquidity as a precautionary measure
Leveraging and Hedging: RBI aims to leverage and hedge by purchasing bonds and securities from commercial banks and Offering them cash in return for the deposited Collateral
Securities and Collaterals: The RBI accepts securities in the form of bonds, gold, and more
Short-Term Borrowing: The central bank lends money for a short period, the maximum being a day. After this, banks generally purchase their deposited securities at a prearranged price
Talk to our investment specialist
How is the Repo Rate Important?
The repo rate is one of the RBI’s monetary policies. The RBI governor oversees the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) bi-monthly meetings. It generally comprises six members. Together, they formulate, manage and edit the policy rates. The RBI modifies it as per the surplus in the nation or liquidity crunch. There are a few parts of repo rate transaction between the RBI and banks, as mentioned below:
- There is a legal agreement through which RBI lends money to the banks that need collateral. It can be bonds and securities. RBI leverages and hedges against securities from commercial banks to lend money
- Repo rate transactions or loans are short-term borrowings. Banks get term or overnight funds, while the RBI gets securities
- Banks can rebuy securities on a certain date and price, which is predetermined. This price refers to the interest amount and loan amount calculated on it at the repo rate
- Banks take money to Handle deficiency of cash reserves. Sometimes, they take money to maintain a minimum reserve balance as a measure of statutory
- RBI authorises the selling of securities if the bank becomes a defaulter and fails to repay the cash on a specific date
How RBI Calculates the Repo Rate?
The RBI regulates the repo rate based on Economic Conditions. The central bank decides this rate based on Recession or inflation in the country’s market.
Impact of Repo Rate on a Common Man
The impact of the repo rate on the life of a common man is nothing but directly associated with an increase in the interest rate. When the repo rate experiences an increase, there is an increase in the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the central bank, making the borrowing process costlier. This forces commercial banks to increase lending rates to handle the increase in the repo rate. Therefore, when a common man borrows a loan from a commercial bank, the interest rate becomes, and the person ends up paying a higher interest amount for the borrowed money.
Relationship Between Inflation and Repo Rate
As you would already know, the Central Bank of India regulates the money supply in the Indian market. A higher repo rate decreases borrowing power, which decreases the cash flow in the market. This methodology helps control inflation.
Let’s understand it further with an example. Suppose India is hit by inflation and RBI has set a 10% repo rate. In such a situation, if commercial banks borrow Rs. 10,000 from the central bank, the interest amount will be Rs. 1,000. To avoid the payment of this interest rate, commercial banks will not borrow anything from RBI, thereby decreasing cash supply in the market. As the cash flow decreases in the market, the demand will not be met. This will help keep inflation in check and control it accordingly.
Impact of Repo Rate on Home Loan
Those who take a Home Loan associated with repo rates or have moved an existing home loan to it must understand a few details about such loans. To begin with, transmissions are quicker. Any adjustments or modifications to the repo rate will likely reflect in the EMI outlay more quickly. This also means that your home loan emi may increase if the bank modifies the benchmark lending rate. Moreover, the bank may decide how much additional interest they will add to the loan repo rate.
Impact of Repo Rate on Fixed Deposits (FDs)
An increase in repo rate could be beneficial for those looking for FDs with competitive rates and low risk. Generally, FDs are anticipated to appreciate in their value as investments. Any change to the policy of repo rate impacts deposit rates and bank lending. Several NBFCs and banks will decide on real rate modifications.
Impact of Repo Rate on the Stock Market
Stock market and interest rates have an inverse relationship. Each time the repo rate experiences an increase, the stock markets get instantly impacted. This simply means that a hike in the repo rate leads businesses to decrease their expense on expansion, which makes the growth a gradual process, impacts future cash flows and profits, and decreases the prices of stocks.
Similarities and Dissimilarities Between Bank Rate and Repo Rate
For RBI, both bank rate and repo rate are important tools when it comes to monitoring money flow and economic activity in the market. However, the difference between them is the promise of government securities to the RBI for a loan.
Here are some similarities and differences between the bank rate and the repo rate:
Similarities
Both of them have an effect on liquidity and regulate the inflation rate. Financial institutions and banks should pass the advantages of interest rate cuts to customers. Thus, they must lower the base rate, which is the lowest rate of interest at which banks lend money to customers. The RBI comes up with the standard rate of interest for every commercial bank. When there is a decrease in the base lending rate, loans become affordable, and EMIs decrease as well.
Dissimilarities
- Financial institutes and commercial banks borrow money at bank rates without any security. Securities are only used as collateral in the repo rate
- Typically, loans with bank rates are available for a longer time period, and the repo rate is for a shorter time period
- Usually, the repo rate is lower than the bank rate as the RBI gives loans without collateral in the bank rate
- The bank rate directly influences the loan rate, and the repo rate impacts huge loans, such as home loans
Difference Between Repo Rate and Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate
The Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR) is referred to a rate used internally for determining the interest rate that banks can levy on their loans. On the other hand, the repo rate is comprehended by the RBI and is charged against funds that commercial banks and other financial institutions borrow from the RBI.
Wrapping Up
RBI makes use of the repo rate as a control measure to handle inflation and create a balance in the economy. The central bank takes up the contrary position in case there is a fall or rise of inflationary pressures. Repo rate hike assists in contracting the economy when the price increase is going beyond. Repo rate also boosts the economy when the same is cooling off the moment rates go low.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What loan types get affected by a decrease or increase in repo rates?
A: A decrease or increase in the repo rate impacts a variety of loans, such as gold loans, home loans, vehicle loans, and personal loans.
2. How often do banks modify loan interest rates tied to the repo rate?
A: As per the guidelines established by the RBI, interest rates that are based on an external benchmark interest rate should be revised every three months.
3. When is the repo rate decided?
A: The RBI’s monetary policy committee decides the RR every two months.
4. Why didn’t the central bank change the repo rate?
A: The repo rate is altered as per the inflation rate and the liquidity position. The RBI has not changed it because a rate cut is going to intensify the post-pandemic inflation existing in a few sectors. Also, a rate hike will hinder the flow of money in the market, which is needed to pace up the economy after the lockdown.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.
You Might Also Like


Everything You Should Know About Fixed Rate Of Interest On Home Loan


Coronavirus Outbreak: Loan Emis On Hold, No RBI Cuts Repo Rate By 75 Bps, Injects Liquidity

RBI Mpc Update: Repo Rate Cut After 5 Years – Impact On Home Loan Emis And Investments
Fixed-rate Of Interest Vs Floating Rate Of Interest- Which Is Better?





