Table of Contents
- Who Can File ITR 3 Form?
- Who Cannot Go for ITR 3 Filing?
- The Structure of ITR-3 Form for AY 2019-20
- How Can You File ITR 3?
- Wrapping Up
- FAQs
- 1. Who has to file the ITR-3?
- 2. What are the exact income heads under which I should file ITR-3?
- 3. Can I file ITR-3 online?
- 4. Does the IT department accept the ITR-3 by mail?
- 5. Is it necessary to mention the nature of business while filing ITR-3?
- 6. Do individuals who have opted for presumptive taxation have to file ITR-3?
- 7. Is Aadhar mandatory for ITR-3?
- 8. What are the liabilities that I have to declare in ITR-3?
- 9. What is unexplained income?
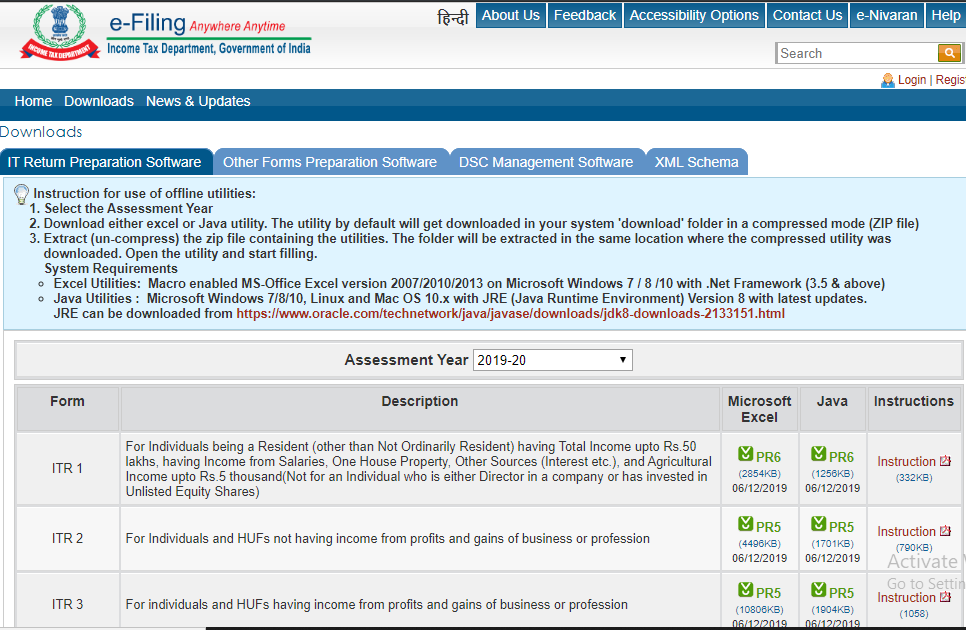
Are you Eligible to File ITR 3? Here's How you Can File ITR 3 Form Online
As per the law, if you fall under the ITR benchmark, then it is mandatory for you to file the return. Since the rules and regulations for taxpayers differ as per their Income and source, the type of form also varies as per the guidelines. Having said that, this post will help you figure out everything about ITR 3 and how can you file it online.
Who Can File ITR 3 Form?
Basically, as far as ITR 3 eligibility is concerned, it can be filled up by the following people:
- A Hindu Undivided Fund or an individual who has a partnership in a firm
- An individual with income from pension or salary
- An individual with Income from house property
- If the taxpayer is registered under Presumptive Taxation.scheme and has an annual turnover of more than 2 crore
- Hindu undivided funds or individuals who have a partnership in a firm, but don’t carry any sort of business under proprietorship; the income from bonus, salary, interest, commission, or remuneration from the associated firm is counted
Who Cannot Go for ITR 3 Filing?
Such individuals or Hindu Undivided Funds who gain their income from a profession or a business as partners cannot file this form type. Such people are required to File ITR 2.
The Structure of ITR-3 Form for AY 2019-20
If you are wondering How to File ITR 3 for AY 2019-20, you must get familiar with the structure of the form to move forward. It has been divided into different parts, such as:
- ITR 3 Part A–GEN: General information and nature of business

ITR 3 Part A-BS: Balance Sheet as of the financial year of the proprietary business or profession
ITR 3 Part A: Manufacturing Account: Manufacturing account for the financial year
ITR 3 Part A: Trading Account: Trading account for the financial year
ITR 3 Part A-P&L: Profit and loss for the financial year
ITR 3 Part A – OI: Other information (optional)
ITR 3 Part A – QD: Quantitative Details (optional)
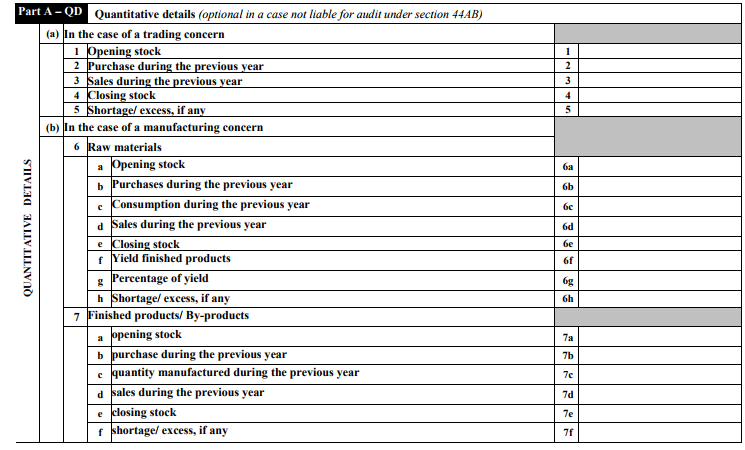
The form continues with the following schedules:
- Schedule – S: Details of income from salaries
Schedule – HP: Calculation of income under the head income from house property
Schedule BP: Calculation of income from business or profession
Schedule – DPM: Calculation of Depreciation on plant and machinery
Schedule DOA: Calculation of depreciation on other assets
Schedule DEP: Summary of depreciation on assets
Schedule DCG- Calculation of deemed Capital gains on the sale of depreciable assets
Schedule ESR: Deduction under section 35
Schedule-CG: Calculation of income under the head Capital Gains
Schedule-OS: Calculation of income under the head income from other sources
Schedule-CYLA: Details of income after set-off of current year’s losses
Schedule BFLA: statement of income after set off of unabsorbed loss brought forward from earlier years
Schedule CFL: Statement of losses to be carried forward to future years
Schedule- UD: Statement of unabsorbed depreciation
Schedule ICDS: Effect of Income Computation Disclosure Standards on Profit
Schedule- 10AA: Calculation of deduction under section 10AA
Schedule 80G: Statement of donations entitled for deduction under Section 80G
Schedule RA: Statement of donations to research associations entitled for deduction under section 35(1) (ii) / 35(1) (IIA) / 35(1) (iii) / 35 (2AA)
Schedule- 80IA: Calculation of deduction under section 80IA
Schedule- 80IB: Calculation of deduction under section 80IB
Schedule- 80IC/ 80-IE: Calculation of deduction under section 80IC/ 80-IE
Schedule VIA: Statement of deductions under Chapter VIA
Schedule AMT: Calculation of Alternate Minimum Tax Payable under Section 115JC
Schedule AMTC: Calculation of tax credit under section 115JD
Schedule SPI: Statement of income arising to spouse/ minor child/ son’s wife or any other person or association of persons
Schedule SI: Statement of income which is chargeable to tax at special rates
Schedule-IF: Information regarding partnership firms
Schedule EI: Statement of Income not included in total income
Schedule PTI: Pass-through income details from a business trust or investment fund as per section 115UA, 115UB
Schedule FSI: Details of income from outside India and tax relief
Schedule TR: Statement of tax relief claimed under section 90 or section 90A or section 91
Schedule FA: Statement of Foreign Assets and income from any source outside India
Schedule 5A: Information regarding apportionment of income between spouses governed by Portuguese Civil Code
Schedule AL: Asset and Liability at the end of the year
Schedule GST: Information regarding turnover/ gross Receipt reported for GST
Part B: Overview of total income and tax calculation of income chargeable to tax
Talk to our investment specialist
Tax Payments
Details of Advance Tax, TDS, self-assessment tax
How Can You File ITR 3?
Unlike other forms, ITR 3 can only be filed online. To do so, follow the below-mentioned steps:
- Go to the government website of the income tax Department
- Log into your dashboard and click Prepare and submit ITR form
- Choose ITR-Form 3
- Add in your details and click Submit
- If applicable, upload your digital signature certificate (DSC)
- Click submit
Wrapping Up
Now that the eligibility for filing ITR 3 is cleared, you can easily figure out whether you should be choosing this form or not. So, move on and find out more about the Income Tax Return form before time runs out of your hand.
FAQs
1. Who has to file the ITR-3?
A: ITR-3 is filed by individuals or hindu undivided family (HUF) members that earn an income from proprietary businesses or professions. This income has to be in the form of gains or profits earned from the profession or the business. It is not filed by individuals whose HUFs earn an income through partnerships with business enterprises. The ITR-3 is only for the profits or gains earned through a proprietary business transaction.
2. What are the exact income heads under which I should file ITR-3?
A: You will be filing ITR-3 if you have made Earnings under the following conditions:
- Income earned in the form of profit or gain from propriety business
- Income earned from house or property
- If the income can be taxed as profits and gains earned as business or profession or professions, for example, interest, salary, bonus, commission or remuneration
Thus, it is essential to check which headings your income falls under and then file an ITR accordingly.
3. Can I file ITR-3 online?
A: Yes, you can file ITR-3 online. You can file it online with the help of a digital signature. You can also file it by submitting a verification code which is generated electronically.
4. Does the IT department accept the ITR-3 by mail?
A: Yes, you can also send the completed ITR-3 data by mail to the Income Tax Department. You will have to post the completed ITR-3 to Post Bag No. 1, Electronic City Office, Bengaluru–560100 (Karnataka).
5. Is it necessary to mention the nature of business while filing ITR-3?
A: Yes, when you file ITR-3, you will have to mention the nature of your business. You will have to give the code of your business, the proprietorship's trade name, and the description of your business. You will also have the provide details of your balance sheet filed as of 31st March of the given financial year.
6. Do individuals who have opted for presumptive taxation have to file ITR-3?
A: No, if you are opting to file Income Tax Returns under presumptive taxation for income earned under business or profession, then you need to file ITR-4 and not ITR-3.
7. Is Aadhar mandatory for ITR-3?
A: Yes, it has become compulsory since 2018-19 to provide your Aadhar details while filing ITR-3.
8. What are the liabilities that I have to declare in ITR-3?
A: When you file ITR-3, you will have to declare value assets and liabilities if the total income from these exceeds Rs.50 lakhs. You will also have to declare all your other immovable property such as houses, jewelry, and gold bullion. If you have profit earning from other assets such as shares and Debentures, you will have to declare them.
9. What is unexplained income?
A: If you have any particular income, such as credit-earning or investment earning, you can categorize this as unexplained income. This income should not be less than Rs.10 lakhs to be mentioned in ITR-3. Otherwise, you can opt for ITR-1 Sahaj for income tax filing.
All efforts have been made to ensure the information provided here is accurate. However, no guarantees are made regarding correctness of data. Please verify with scheme information document before making any investment.